Explore proven methods, nutritional tips, and the latest research to take control of your diabetes. Cure Diabetes

Effective Strategies for Curing Gestational Diabetes: Your Ultimate Guide

How to Cure Prediabetes Permanently, Naturally and Fast at Home

How to Cure Type 1 Diabetes Permanently, Naturally at Home with diet and exercise

How to Cure Type 2 Diabetes Permanently, Naturally and Fast with Diet and Exercise

How to Cure Type 3 diabetes

How to Manage Diabetes: A Comprehensive Approach. Cure Diabetes
Is it possible to cure diabetes?
The term "cure" can be misleading. While there isn't a definitive cure, diabetes can be managed effectively through various approaches.
Understanding Diabetes. Cure Diabetes
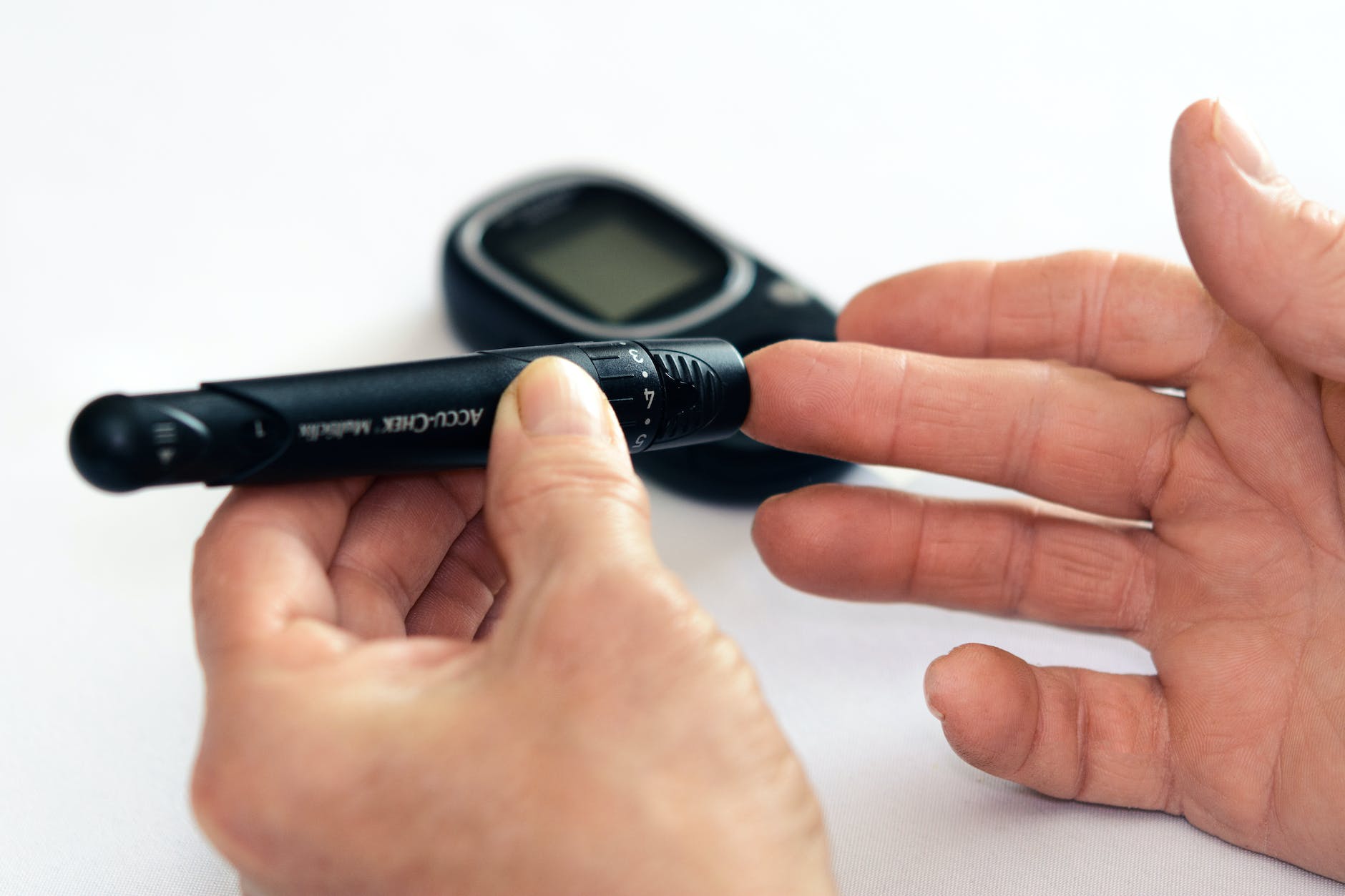
Different Varieties of Diabetes: Explained for Better Understanding
Explore the differences between Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes to understand their unique characteristics and challenges.
See More Now...
Symptoms and Complications
Recognizing the signs of diabetes early can prevent complications. Learn about the symptoms and potential health risks associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
See More Now...Dietary Changes for Managing Diabetes. Cure Diabetes
Low-Calorie Diets
Low-calorie diets can play a crucial role in managing diabetes. Discover the benefits and considerations of reducing calorie intake.
See More Now...
Recommended Foods and Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels while others might cause spikes. Learn which foods to embrace and which to avoid.
See More Now...Weight Loss and Diabetes Management. Cure Diabetes

How Much Weight Do I Need to Lose?
Weight loss can improve diabetes management. Find out how much weight loss is beneficial and set realistic, healthy goals.
See More Now...
Exercise and Diabetes
Regular physical activity is vital in managing diabetes. Explore various exercises that are safe and effective for individuals with diabetes.
See More Now...Medical Treatments and Surgeries. Cure Diabetes
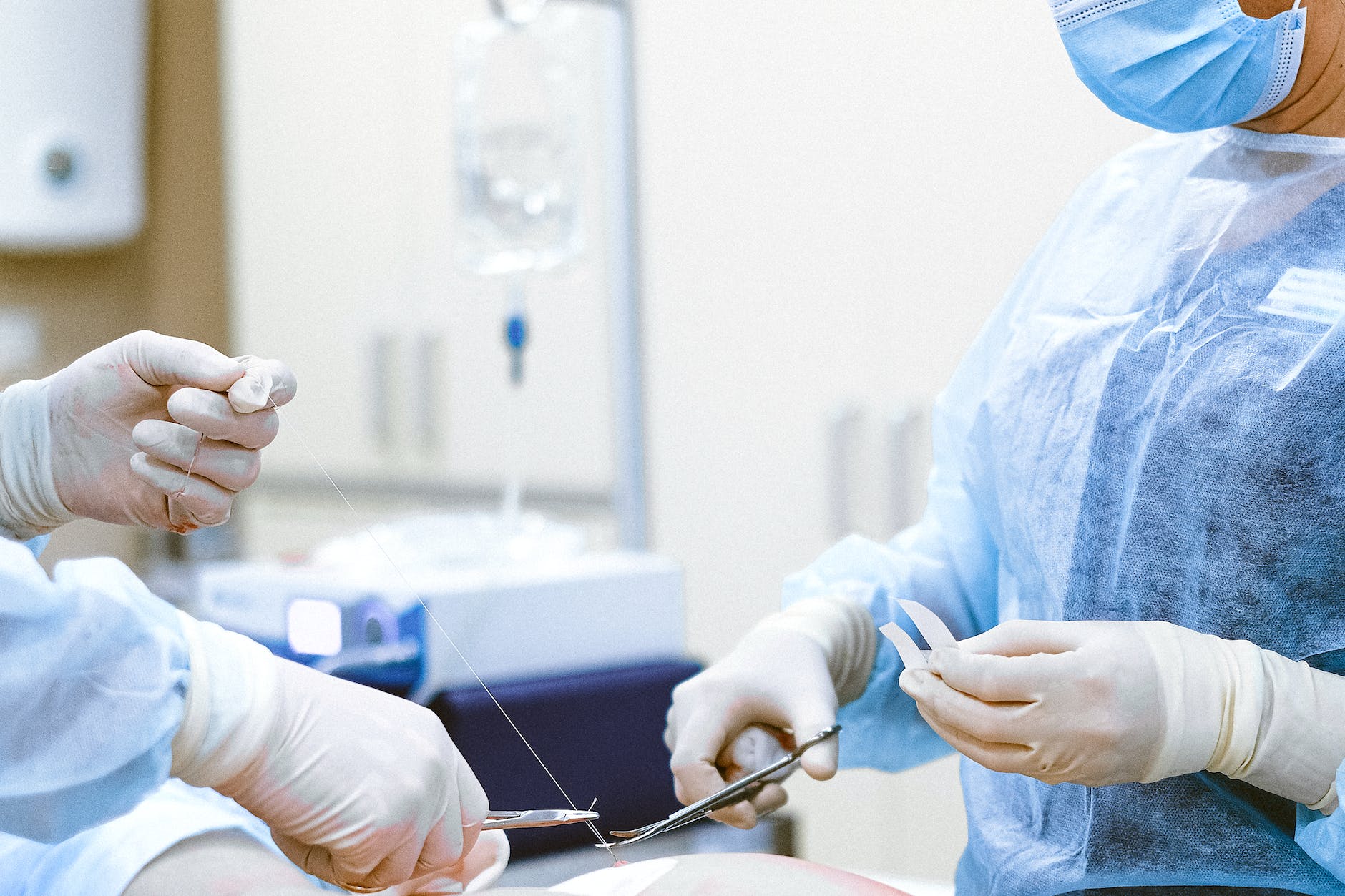
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery may help some individuals manage diabetes more effectively. Understand the risks and benefits associated with this surgical procedure.
See More Now...
Medications and Supplements
Medications and supplements can be essential for diabetes care. Familiarize yourself with the various options available and how they work.
See More Now...Alternative Therapies. Cure Diabetes

Therapeutic Fasting
Fasting may offer benefits in regulating blood sugar levels. However, it's not suitable for everyone. Discover if therapeutic fasting is right for you.
See More Now...
Natural Therapies
Natural therapies can complement traditional diabetes treatments. Learn about herbs, supplements, and other holistic approaches that may aid in managing diabetes.
See More Now...Research and Future Advancements. Cure Diabetes

Stem Cells and Diabetes
Stem cell research shows promise in the field of diabetes management. Stay updated on the latest breakthroughs and potential future treatments.
See More Now...
Islet Cell Transplantation
Islet cell transplantation is a procedure under research that might help in managing diabetes. Learn about the process, benefits, and risks associated with it.
See More Now...Conclusion

Next Steps
Managing diabetes requires a multifaceted approach. Follow these next steps to embark on your journey to effective diabetes management.
See More Now...
Consult with Your Doctor
Before making any changes to your diabetes care plan, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that it’s safe and appropriate for your unique health profile.
See More Now...How To Cure Diabetes: Effective Strategies for Managing Your Health. Cure Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic illness that affects insulin production and utilization in the body, leading to high blood sugar levels. While there is no definitive cure, there are various ways to manage and treat diabetes, particularly type 2. Dietary changes and weight loss have been shown to successfully reverse type 2 diabetes in some individuals. Exercise also plays a crucial role. Surgical options, natural remedies, and alternative therapies offer additional avenues for diabetes management and potential remission. Understanding these approaches can help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
Understanding Diabetes and its Impact on Health. Cure Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body's ability to produce or effectively utilize insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. It has a profound impact on an individual's overall health and can lead to serious complications if not managed properly.
What is Diabetes and How Does it Affect the Body?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. The two main types of diabetes are Type 1 and Type 2. In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar effectively.
The elevated blood sugar levels in diabetes can have significant effects on various organs and systems in the body. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can cause damage to the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. It increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, retinopathy, neuropathy, and other serious complications.
Types of Diabetes: Exploring Type 1 and Type 2
Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, usually develops in childhood or early adulthood. It requires daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump to manage blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes is not preventable and its exact cause is still unknown.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is more prevalent and commonly associated with lifestyle factors such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity. It can usually be managed with a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, oral medication, or insulin therapy if necessary.
The Importance of Managing Diabetes for your Health
Effectively managing diabetes is crucial to prevent or delay complications and maintain a good quality of life. By taking control of blood sugar levels and implementing lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of complications.
Proper management of diabetes includes monitoring blood sugar levels, following a balanced and nutritious diet, engaging in regular physical activity, taking prescribed medications as directed, and attending regular medical check-ups. These measures help in maintaining optimal blood sugar control, reducing the risk of complications, and improving overall health and well-being.
Understanding the impact of diabetes on health and the importance of actively managing the condition empowers individuals to make informed decisions and take control of their well-being. With the right strategies, support, and adherence to recommended treatments, living a healthy and fulfilling life with diabetes is not only possible but achievable.
How to Cure Type 2 Diabetes Permanently. Cure Diabetes
When it comes to effectively managing and potentially reversing Type 2 diabetes, there are several key strategies to consider. From making dietary changes to implementing weight loss strategies and incorporating regular exercise, taking a comprehensive approach can make a significant impact on your health.
Dietary Changes for Reversing Type 2 Diabetes
One of the most crucial steps in reversing Type 2 diabetes is adopting a healthy and balanced diet. By making thoughtful food choices, you can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Here are some essential dietary changes to consider:
- Incorporate more whole, unprocessed foods into your meals, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid sugary beverages and processed foods that are high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates.
- Focus on consuming foods with a low glycemic index, which have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
- Monitor portion sizes and practice mindful eating to prevent overeating and promote weight loss.
Weight Loss Strategies and their Role in Type 2 Diabetes Remission
Weight loss plays a significant role in reversing Type 2 diabetes. Shedding excess pounds can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition. Consider the following strategies for successful weight loss:
- Set realistic goals for weight loss, aiming for gradual and sustainable progress.
- Adopt a calorie-controlled diet that creates a calorie deficit for weight loss.
- Engage in regular physical activity to enhance calorie burning and support weight loss efforts.
- Seek guidance from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians to tailor a weight loss plan according to individual needs.
Exercise and Physical Activity for Controlling Type 2 Diabetes
Regular exercise is crucial for managing and potentially reversing Type 2 diabetes. Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and promote overall cardiovascular health. Consider the following guidelines for incorporating exercise into your routine:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Include strength training exercises at least two days a week to build muscle and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Seek guidance from a healthcare professional or a certified exercise specialist to develop an exercise plan that is safe and tailored to your health and fitness level.
By combining dietary changes, weight loss strategies, and regular exercise, you can take proactive steps towards managing and potentially reversing Type 2 diabetes. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance to ensure safe and effective diabetes management.
How to Cure Type 1 Diabetes Permanently. Cure Diabetes
Living with type 1 diabetes can be challenging due to the lifelong dependence on insulin injections and the constant need for blood sugar monitoring. While there is currently no known cure for type 1 diabetes, several management options are available to help individuals lead fulfilling lives while effectively controlling their condition.
Understanding the Challenges of Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
Managing type 1 diabetes involves carefully monitoring blood sugar levels, adjusting insulin doses, and maintaining a balanced diet. The challenges lie in the complexities of insulin therapy, the risk of hypoglycemia, and the potential long-term complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Current Options for Managing Type 1 Diabetes
The primary treatment for type 1 diabetes is injected insulin, typically administered through insulin pens or insulin pumps. Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels, carbohydrate counting, and regular exercise are essential components of diabetes management. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices provide real-time data to help individuals make informed decisions regarding insulin dosing and lifestyle adjustments.
Promising Research and Potential Cures for Type 1 Diabetes
Researchers are actively exploring potential cures for type 1 diabetes, with a focus on regenerative medicine and immunotherapy. Islet cell transplantation, where insulin-producing cells are transplanted into the recipient's body, shows promise in restoring insulin production. Additionally, advancements in stem cell research and gene therapy offer hope for future treatments to halt the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells.
While a definitive cure for type 1 diabetes remains elusive, ongoing research and technological advancements provide hope for improved management and potential breakthroughs in the future.
Natural Approaches to Cure Diabetes in 30 Days. Cure Diabetes
When it comes to managing diabetes, natural remedies and alternative therapies can play a significant role in supporting overall health and controlling blood sugar levels. These approaches can complement conventional treatment methods and offer additional benefits to individuals with diabetes.
Exploring Natural Remedies and Alternative Therapies for Diabetes
There are various natural remedies and alternative therapies that have shown promise in helping individuals with diabetes manage their condition effectively. Some of these include:
- Herbal supplements and botanical extracts: Certain herbs and plant-based substances have been found to have potential blood sugar-lowering effects. Examples include cinnamon, bitter melon, fenugreek, and Gymnema sylvestre.
- Aromatherapy: The use of essential oils, such as lavender and cypress, in aromatherapy practices may help promote relaxation, reduce stress levels, and support overall well-being.
- Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese therapy involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and promote balance. Research suggests that acupuncture may help manage diabetes symptoms and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Mind-body techniques: Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress, improve insulin sensitivity, and enhance overall mental and physical well-being.
The Role of Diet and Nutrition in Natural Diabetes Management
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in managing diabetes naturally. Making healthy food choices and following a balanced eating plan can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall health. Consider the following tips:
- Eat a variety of nutrient-dense foods: Include a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and heart-healthy fats in your diet.
- Avoid processed foods and sugary beverages: Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages that can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Focus on portion control: Pay attention to portion sizes to prevent overeating and manage your calorie intake.
- Choose low-glycemic index foods: Opt for foods that have a lower impact on blood sugar levels, such as whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables.
- Stay hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to support proper hydration and overall health.
Lifestyle Modifications for Promoting Long-term Diabetes Control
In addition to diet and natural remedies, certain lifestyle modifications can contribute to long-term diabetes control. Consider incorporating the following habits into your daily routine:
- Regular physical activity: Engage in regular physical exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, to improve insulin sensitivity, manage weight, and promote overall cardiovascular health.
- Stress management: Practice stress-relief techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or hobbies that help you relax and reduce stress levels, as prolonged stress can negatively impact blood sugar control.
- Adequate sleep: Aim for seven to eight hours of quality sleep every night to support proper hormone regulation and overall well-being.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Moderate your alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol consumption can affect blood sugar levels and interfere with diabetes management.
- Regular monitoring: Regularly check your blood sugar levels and keep track of any changes or patterns with the help of your healthcare provider.
By implementing these natural approaches and making positive lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can work towards better managing their condition and promoting overall health and well-being.
Surgical Solutions for Diabetes Remission. Cure Diabetes
As medical advancements continue to progress, surgical interventions have emerged as potential solutions for achieving diabetes remission, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes. This section explores the overview of bariatric surgery as a treatment option and delves into how bariatric surgery affects weight loss and diabetes control. Additionally, it highlights the considerations and risks associated with bariatric surgery for patients with diabetes.
Overview of Bariatric Surgery as a Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, involves altering the anatomy of the digestive system to assist in weight loss and potentially reverse type 2 diabetes. This surgical procedure restricts the stomach's capacity, reducing the amount of food an individual can consume. It can also modify the digestive process to limit calorie absorption.
Studies have shown that bariatric surgery can significantly improve glycemic control and lead to long-term remission of type 2 diabetes in many patients. By inducing weight loss and altering gut hormones, this surgery addresses the underlying metabolic abnormalities associated with diabetes.
How Bariatric Surgery Affects Weight Loss and Diabetes Control
Bariatric surgery promotes weight loss by restricting food intake or causing malabsorption, resulting in reduced caloric intake. This sustained weight loss leads to improved insulin sensitivity and glucose utilization by the body. Additionally, the surgery triggers changes in gut hormones, such as incretin production, which contribute to better blood sugar regulation.
Not only does bariatric surgery aid in weight loss, but it also has a positive impact on other comorbidities associated with type 2 diabetes, such as high blood pressure and hyperlipidemia. By addressing these underlying health conditions, bariatric surgery improves overall health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Considerations and Risks of Bariatric Surgery for Diabetes Patients
While bariatric surgery offers potential benefits for diabetes remission, it is essential to consider various factors and understand the associated risks. Patients undergoing this procedure should have a comprehensive understanding of the surgery's effects, the potential complications, and the necessary lifestyle changes post-surgery.
Some potential risks and complications of bariatric surgery include infection, bleeding, malnutrition, and the need for long-term vitamin and mineral supplementation. It is crucial for individuals considering this surgical option to consult with healthcare professionals specializing in bariatric surgery to assess their eligibility and discuss the potential risks and benefits.
In Conclusion
Bariatric surgery presents an alternative approach to achieve remission of type 2 diabetes by promoting weight loss and addressing metabolic abnormalities. While it can be an effective solution, thorough consideration of the procedure's implications and potential risks is necessary. Consulting with healthcare professionals is vital to make informed decisions and determine if bariatric surgery is a suitable option for managing and potentially reversing diabetes.
Chris bumstead kidney disease. Cure Diabetes
The journey towards understanding and managing diabetes often intersects with the personal health challenges faced by public figures, which can inspire and educate the wider community. A pertinent example is the Canadian professional bodybuilder Chris Bumstead, who has been open about his battle with a kidney condition known as IgA nephropathy, or Berger's disease. This autoimmune kidney disease can affect individuals differently, but it's particularly concerning for those with diabetes, as diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease. Bumstead's proactive approach to managing his health condition provides valuable insights into how one can strive for wellness despite the hurdles posed by such chronic diseases.
- IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease): A condition where an antibody called immunoglobulin A (IgA) builds up in the kidneys, leading to inflammation that can hamper the kidneys' ability to filter waste from the blood.
- Chris Bumstead's diagnosis: He was diagnosed with this condition prior to winning his first Classic Physique Olympia title, showcasing that with proper management and determination, one can still achieve great success.
- Impact on bodybuilders: Kidney diseases can be particularly challenging for bodybuilders due to the high-protein diets and intense training regimens that can strain the kidneys.
- Management strategies: Chris Bumstead has discussed various strategies he uses to manage his condition, including careful diet planning, regular medical checkups, and monitoring his protein intake.
- Lifestyle modifications: His approach emphasizes the importance of adapting one's lifestyle to support kidney health, which can also be beneficial for those managing diabetes.
- Education and awareness: By sharing his story, Bumstead raises awareness about kidney health, encouraging others to stay informed and proactive about their conditions.
Chris bumstead disease. Cure Diabetes
Chris Bumstead, a renowned IFBB professional bodybuilder, has brought significant attention to a condition known as Thalassemia. While not related to diabetes, his journey with this health challenge has been an inspiration for many in the fitness community. Thalassemia is a blood disorder that affects the body's ability to produce hemoglobin and red blood cells, leading to anemia. Bumstead's openness about his condition has highlighted the importance of proper health management and how chronic conditions can be managed alongside a demanding career. His success in bodybuilding despite his condition serves as a motivating story for those looking to overcome their own health battles, including managing diabetes.
- Understand Your Condition: Knowledge is power when it comes to managing chronic diseases.
- Regular Check-Ups: Consistent monitoring can help track the progress and manage the condition effectively.
- Proper Diet and Nutrition: Tailoring your diet to meet specific health needs is crucial in managing chronic conditions.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise plays a significant role in overall health and can help in managing symptoms.
- Medication Adherence: Staying on top of any prescribed medications is vital for keeping the condition under control.
- Mental Health Support: Chronic conditions can take a toll on mental health, so seeking support is important.
- Educating Others: Sharing your experience can help build awareness and support for others with similar conditions.
Remember, while there is currently no cure for diabetes, these strategies can be effective in managing the condition and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It's always important to consult with healthcare professionals to create a personalized plan that works for you.
Chris bumstead kidney disease. Cure Diabetes
Among the myriad of health challenges faced by individuals today, Chris Bumstead's kidney disease serves as a poignant example of the fact that even the fittest individuals are not immune to health issues. Chris, a renowned bodybuilder and three-time Mr. Olympia Classic Physique winner, has been open about his struggles with a form of kidney disease known as IgA nephropathy, or Berger's disease. His journey underscores the importance of vigilant health management, especially in the context of chronic conditions like diabetes, where the risk of kidney complications is heightened. Understanding how Chris has approached his health can provide valuable insights for those looking to manage their diabetes with effective strategies. Here is a list of elements related to Chris Bumstead's kidney disease:
- IgA Nephropathy (Berger's Disease): The specific type of kidney disease Chris Bumstead has been diagnosed with, which affects the glomeruli within the kidneys.
- Early Detection: Chris's condition was identified early, emphasizing the importance of regular health check-ups for early detection of kidney issues.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: After his diagnosis, Chris had to make significant changes to his diet and exercise routines to accommodate his kidney health.
- Medication and Treatment: Managing kidney disease often involves a combination of medications and treatments to control symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Monitoring Kidney Function: Regular monitoring of kidney function through blood tests and other diagnostics is crucial for individuals with kidney disease, including those with diabetes.
- Education and Awareness: By sharing his experience, Chris has raised awareness about kidney disease and the importance of health management among his audience.
Chris bumstead disease. Cure Diabetes
When discussing effective strategies for managing health with diabetes, it is important to acknowledge the diverse challenges individuals may face, including those encountered by public figures such as Chris Bumstead. Known for his impressive physique and status as a Classic Physique Mr. Olympia champion, Bumstead has been open about his journey with Type 1 diabetes. This autoimmune disease, which affects the pancreas's ability to produce insulin, poses unique management hurdles. Bumstead's approach to tackling his condition has been an inspiration for many, showing that with the right strategies and determination, one can thrive despite a diabetes diagnosis. The following list outlines several key elements associated with managing diabetes effectively, reflecting the kind of diligence seen in Bumstead's regimen:
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Keeping a close eye on blood glucose levels to make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
- Insulin Therapy Adherence: For those with Type 1 diabetes like Chris Bumstead, following a strict insulin regimen is crucial for glucose regulation.
- Dietary Management: Consuming a balanced diet that helps to maintain steady blood sugar levels, incorporating a mix of macronutrients and fiber.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise, which can improve insulin sensitivity and help control blood sugar levels.
- Stress Reduction: Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or other relaxation practices, as stress can affect blood glucose control.
Incorporating these elements into one's daily routine, as Chris Bumstead has done, can be instrumental in leading a healthy and fulfilling life with diabetes.

