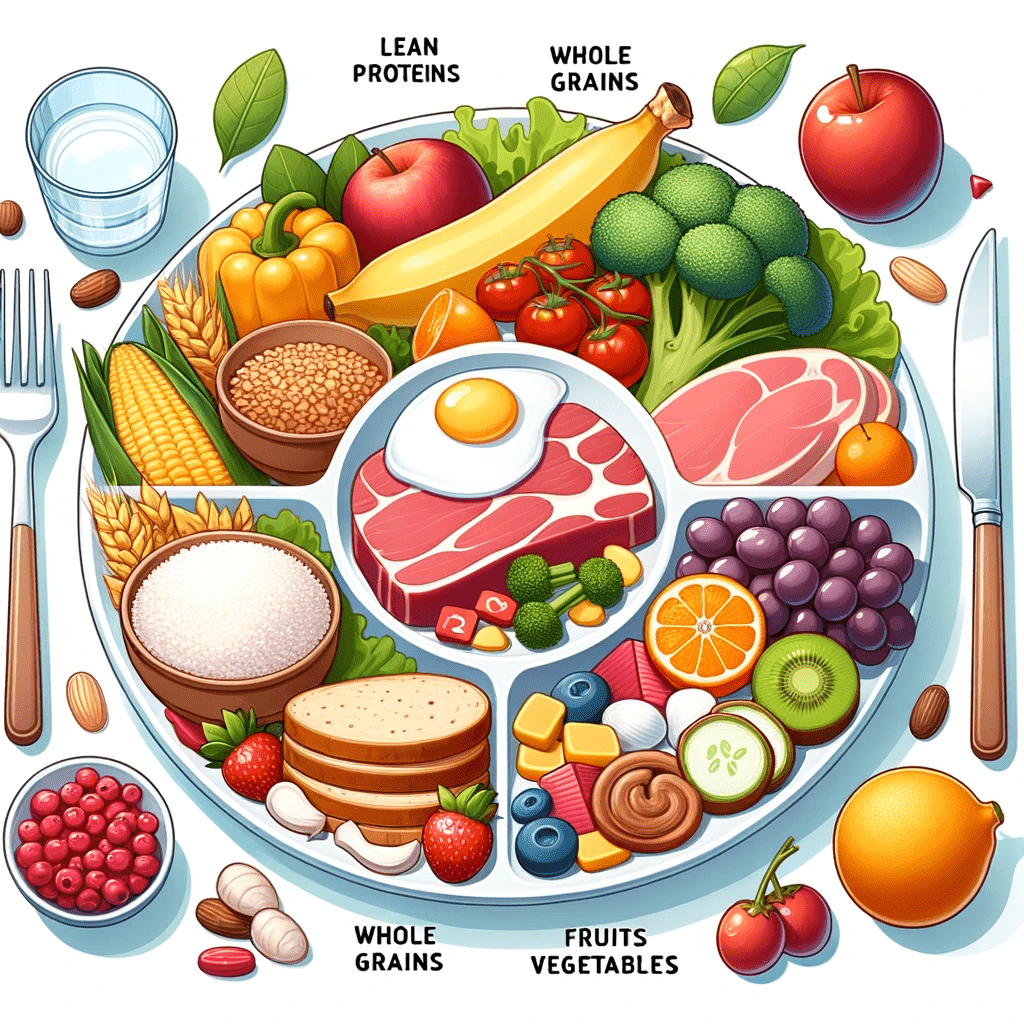How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide

Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that cannot be cured, but there are ways to manage and potentially achieve remission. Remission means keeping blood sugar levels below the diabetic range for an extended period without medication. Losing weight through low-calorie diets and exercise can help in achieving remission. Bariatric surgery is also a potential option. This article explores the various aspects of managing type 2 diabetes and strategies for achieving remission. Additional resources and support are available for those on their diabetes journey. How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
- Understanding Type 2 Diabetes - How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes - How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
- Achieving Diabetes Remission - How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
- Additional Support and Resources - How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes - How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
Diabetes has become a prevalent and chronic health condition affecting many individuals in the United States. Understanding the nature of type 2 diabetes is vital for effective management and potential remission. This section delves into the fundamental aspects of type 2 diabetes, including its definition, causes and risk factors, symptoms and diagnosis, as well as its impact on overall health.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes, also known as adult-onset diabetes, is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of blood sugar. Unlike type 1 diabetes, the body still produces insulin, but it either doesn't use it effectively or doesn't produce enough. This insulin resistance leads to elevated blood sugar levels and various health complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. These include genetics, sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, obesity, and age. Family history and ethnic background also play a role, as certain groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, are more susceptible to developing the condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of type 2 diabetes is crucial for early detection and management. Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. Diagnosis involves blood tests that measure blood sugar levels, such as fasting blood sugar or the A1C test, which provides an average blood sugar level over the past few months.
The Impact on Overall Health
Type 2 diabetes can have a significant impact on overall health and increase the risk of various complications. These complications include cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, vision problems, and slower wound healing. Diabetes management is essential to minimize these risks and improve overall well-being.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes - How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
Managing type 2 diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on various aspects of your lifestyle. By diligently following these strategies, you can effectively control your blood sugar levels and minimize the risk of complications.
Medication and Insulin Treatment
For many individuals with type 2 diabetes, medication or insulin treatment is a crucial component of their management plan. Your healthcare professional will determine the appropriate medications based on your specific needs, considering factors such as your blood sugar levels, overall health, and any other existing medical conditions.
Blood Sugar Control Techniques
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential in managing diabetes. By using a blood glucose meter, you can track your levels and adjust your treatment plan accordingly. Additionally, techniques like carbohydrate counting, portion control, and timing of meals can help regulate blood sugar levels and maintain stability.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical exercise plays a vital role in managing type 2 diabetes. Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, control weight, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity every week, along with strength training exercises.
Monitoring and Managing Diet
Dietary modifications are crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. Focus on consuming a balanced diet that includes lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat items. Portion control and mindful eating can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle Changes for Weight Management
Weight management is vital in managing type 2 diabetes effectively. Incorporate healthy lifestyle changes such as setting realistic weight loss goals, adopting mindful eating habits, getting adequate sleep, reducing stress levels, and avoiding sedentary behavior. These changes contribute to weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and better overall diabetes control.
Achieving Diabetes Remission - How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
Achieving diabetes remission refers to a state where individuals with type 2 diabetes are able to maintain their blood sugar levels within the normal range for an extended period without relying on medication. This section explores various strategies that have shown promise in achieving remission and improving overall health.
What is Diabetes Remission?
Diabetes remission is defined as successfully managing blood sugar levels below the diabetic range without the need for medication. It is important to note that remission does not mean a complete cure, as there is always a possibility of symptoms returning. However, with the right approach, it is possible to achieve a state of remission and significantly improve overall well-being.
Weight Loss and Diabetes Reversal
Weight loss plays a crucial role in diabetes remission. Studies have shown that shedding excess pounds can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control. By adopting a healthy eating plan and engaging in regular physical activity, overweight individuals with type 2 diabetes can reverse the disease and achieve remission.
Very Low-Calorie Diets and Remission Studies
Very low-calorie diets (VLCDs) have been studied extensively for their impact on diabetes remission. These diets involve consuming 625-850 calories per day for a period of 2-5 months, followed by a less restrictive diet for weight maintenance. Remarkably, nearly half of the participants in these studies achieved diabetes reversal and maintained near-normal blood glucose levels for 6 months to 1 year.
Bariatric Surgery and Its Impact
Bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, is another option for achieving diabetes remission. These procedures help individuals lose weight by altering the stomach and digestive system, thereby limiting food intake. Additionally, they can affect the gut hormones involved in blood glucose regulation. Approximately three-quarters of people who undergo bariatric surgery experience diabetes remission, making it a powerful intervention for those with a high body mass index (BMI) and weight-related health issues like diabetes.
Long-Term Strategies for Sustaining Remission
After achieving remission, it is essential to adopt long-term strategies to sustain it. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adhering to a balanced diet. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals and ongoing support from diabetes organizations and support groups can also play a vital role in successfully managing and sustaining remission.
Additional Support and Resources - How to Permanently Cure Type 2 Diabetes: US Guide
Diabetes Organizations and Support Groups
Achieving diabetes management and remission requires a strong support system. Joining diabetes organizations and support groups can provide invaluable resources and a sense of community. Organizations like the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and JDRF offer educational materials, online forums, and local events to connect with others battling diabetes. Support groups, whether online or in-person, allow individuals to share experiences, gain insights, and receive emotional support from fellow individuals navigating the challenges of type 2 diabetes.
Working with Healthcare Professionals
Collaborating with healthcare professionals is essential for effectively managing type 2 diabetes and aiming for remission. Consult with doctors, nurses, and dietitians to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs. Regular check-ups and blood sugar monitoring help track progress and identify necessary adjustments. Additionally, working with a diabetes educator can provide valuable guidance on lifestyle changes, medication management, and coping strategies for diabetes-related challenges.
Staying Informed about Diabetes Research
Keeping up to date with the latest advancements in diabetes research is crucial in gaining a comprehensive understanding of the condition and available treatment options. Stay informed through reputable sources such as medical journals, research institutions, and diabetes-specific websites. By staying in the loop, you can make informed decisions about your diabetes management, consider new therapies or interventions, and explore potential breakthroughs that may impact your journey towards remission.
Empowering Yourself with Knowledge
Education is key to taking control of your diabetes journey. Arm yourself with knowledge about type 2 diabetes, its causes, symptoms, and management techniques. Learn about dietary choices, exercise regimens, and the importance of weight management. Understanding how medications work and their potential side effects empowers you to make informed decisions about your treatment plan. The more you learn, the more effectively you can work with healthcare professionals and proactively manage your condition.
Taking Control of Your Diabetes Journey
Your journey towards managing and possibly achieving remission of type 2 diabetes is in your hands. Foster a positive mindset and embrace proactive lifestyle changes. Set realistic goals, celebrate small victories, and stay committed to long-term strategies. Implementing healthy habits like regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and stress management are all crucial for achieving and sustaining diabetes remission. Remember, you have the power to make a difference in your health and well-being!