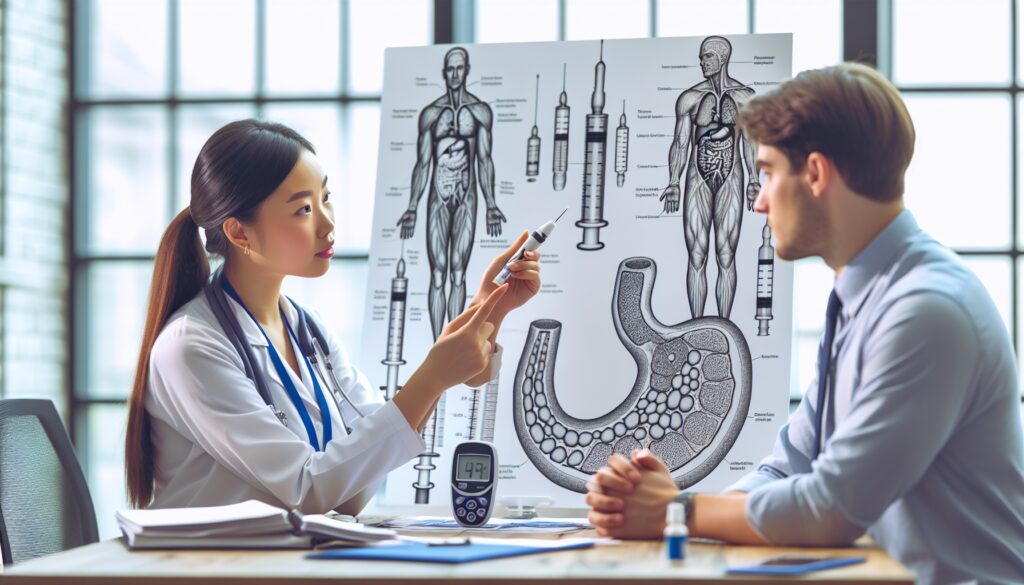
Insulin is a hormone that plays a critical role in our body's ability to use glucose from the food we eat for energy. The pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, produces insulin and releases it into the bloodstream to help regulate blood sugar levels. Without insulin, our body would not be able to properly utilize glucose, leading to elevated levels of sugar in the blood, a condition known as hyperglycemia.
🔍 Seeking a breakthrough in Type 2 Diabetes management?
Discover our expert insights and innovative approaches on ‘How to Cure Diabetes’.
Click to transform your health journey today!
What you\'ll find in this article?
How Does Insulin Work?
When we eat, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose and absorbed into the bloodstream. As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas secretes insulin. Insulin acts as a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose to enter and be used for energy. It also helps store glucose in the liver and muscles for future use and signals the liver to stop producing sugar.
Without insulin, glucose remains in the bloodstream, causing high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can lead to serious health complications like heart disease, kidney damage, and vision impairment.
Understanding how insulin facilitates glucose entry into cells and maintains normal blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes, a condition characterized by chronic high blood sugar.
Explore our specialized services in diabetes care 🌟.
From personalized diet plans to effective exercise routines, we have what you need to take control of Type 2 Diabetes.
Visit our services page now!







What Are the Different Types of Insulin?
There are various types of insulin used to manage diabetes, each with different onset times, peak times, and durations of action. The main types include:
- Rapid-acting insulin, which starts working within minutes after injection and is effective for a few hours.
- Short-acting insulin, which generally starts working within 30 minutes and lasts for 3 to 6 hours.
- Intermediate-acting insulin, which starts working within 2 to 4 hours and can last up to 18 hours.
- Long-acting insulin, which can work for up to 24 hours or more, providing a steady level of insulin.
The type of insulin prescribed depends on the individual's needs, eating habits, and blood sugar patterns. Personalized treatment plans are crucial for effective diabetes management.
What Is Insulin Used For?
Insulin therapy is primarily used for managing diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes produce little to no insulin and must use insulin injections to control their blood sugar levels. Some people with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes may also need insulin therapy if other medications and lifestyle changes cannot adequately control blood sugar levels.
Additionally, insulin is sometimes used in hospitals to manage hyperkalemia, a condition where a person has too much potassium in their blood.
Insulin can also be used in diagnostic tests for growth hormone deficiencies and in research to understand cell metabolism and diabetes.
What Happens When There Is Insufficient Insulin?
Insufficient insulin production or use leads to high blood sugar levels, which can result in symptoms like increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can cause heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and other serious conditions.
In extreme cases, insufficient insulin can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate medical attention.
Consistently high blood sugar levels can also contribute to the development of insulin resistance, where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin.
What Is Insular Resistance?
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin. It can lead to the pancreas producing more insulin to try to get cells to respond, eventually leading to type 2 diabetes if the pancreas can no longer keep up with the demand for insulin.
Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and being overweight can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance, which is often a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Is Insulin Harmful?
While insulin is vital for blood sugar regulation, like any medication, it can have side effects. Insulin side effects can include low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), weight gain, and allergic reactions at the injection site. However, these risks can be minimized with careful dosing, monitoring, and patient education.
It is important to use insulin as prescribed and to work with healthcare providers to adjust dosages as needed. With proper management, insulin can be safely used to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
What Exactly Does Insulin Do?
Insulin helps control blood sugar by allowing glucose to enter cells to be used for energy and by storing excess glucose in the liver. It is essential for maintaining blood sugar regulation and overall metabolic balance.
By promoting the absorption of glucose into tissues such as muscle and fat, insulin prevents excessive sugar buildup in the bloodstream, which is crucial for preventing diabetes-related complications.
What Is Insulin Short Answer?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. It is vital for energy production and maintaining normal blood glucose levels.
What Can Insulin Do to Your Body?
Insulin plays a key role in managing blood sugar and energy use in the body. It helps convert glucose into energy, store it for future use, and keep blood sugar levels within a normal range.
Insulin also affects fat metabolism and can contribute to weight changes when used in diabetes treatment.
Is Sugar and Insulin the Same Thing?
No, sugar and insulin are not the same. Sugar, or glucose, is a type of carbohydrate that serves as an energy source, while insulin is a hormone that helps regulate how the body uses and stores glucose.
Understanding the distinct roles of glucose as an energy source and insulin as a regulatory hormone is important for managing diabetes and maintaining health.
For those seeking a visual explanation of insulin's function, we have selected an informative video:
By understanding everything about insulin, including its types, functions, and usage, individuals can better manage their diabetes and maintain overall health. It's important to consult healthcare providers for personalized advice and treatment plans.
✨ Other articles you might be interested in: