Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition affecting sugar regulation in the body. Insufficient insulin production and poor cell response contribute to the disease. Symptoms may include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and tingling sensations. Managing diabetes involves weight loss, healthy eating, exercise, and possibly medication or insulin therapy. Complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, kidney issues, and eye diseases can arise, emphasizing the importance of prevention strategies through lifestyle changes and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.
🔍 Seeking a breakthrough in Type 2 Diabetes management?
Discover our expert insights and innovative approaches on ‘How to Cure Diabetes’.
Click to transform your health journey today!







What you\'ll find in this article?
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body's sugar regulation. To understand the symptoms of type 2 diabetes, it is crucial to be aware of the risk factors associated with this condition.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Several factors increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. These may include genetic predisposition, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Having a family history of diabetes or belonging to certain ethnic groups can also elevate the risk.
Overview of Blood Sugar and Insulin
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for our cells. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, is essential for regulating blood sugar levels. In type 2 diabetes, the body either produces insufficient insulin or becomes resistant to its effects.
How Cells Respond to Insulin
Insulin resistance is a key factor in type 2 diabetes. When cells become less responsive to insulin, glucose uptake is impaired, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This condition can result in various symptoms and complications if left uncontrolled.
Diagnostic Tests for Diabetes
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes typically involves blood tests to measure fasting blood sugar levels or a glucose tolerance test. Additionally, healthcare providers may assess hemoglobin A1c levels to evaluate long-term blood sugar control. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
Recognizing Common Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
Explore our specialized services in diabetes care 🌟.
From personalized diet plans to effective exercise routines, we have what you need to take control of Type 2 Diabetes.
Visit our services page now!
Understanding and recognizing common symptoms of type 2 diabetes is crucial for early detection and management. Various signs may indicate the presence of diabetes, and being aware of these symptoms can prompt individuals to seek medical advice and necessary treatment.
Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination
One of the classic signs of type 2 diabetes is increased thirst, known as polydipsia, often accompanied by frequent urination, also called polyuria. This occurs as the body tries to eliminate excess sugar through urine, leading to dehydration and a continuous cycle of thirst and urination.
Excessive Hunger and Unintentional Weight Loss
Experiencing intense hunger, even after eating, can signal unstable blood sugar levels commonly seen in diabetes. Additionally, unintentional weight loss may occur due to the body's inability to effectively utilize glucose for energy, resulting in the breakdown of fat and muscle tissues.
Fatigue and Blurred Vision
Feelings of extreme fatigue and tiredness, despite adequate rest, can be indicative of uncontrolled diabetes. Blurred vision may also arise due to changes in fluid levels in the eye caused by high blood sugar levels impacting the lens.
Slow Healing Wounds and Frequent Infections
Individuals with type 2 diabetes may notice that wounds, cuts, or sores take longer to heal than usual. This delayed healing process is a result of poor circulation and compromised immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Tingling Sensation in Hands or Feet
A common symptom of diabetes known as neuropathy, tingling sensations or numbness in the hands or feet can occur due to nerve damage from prolonged high blood sugar levels. This sensation may also spread to other areas of the body over time.
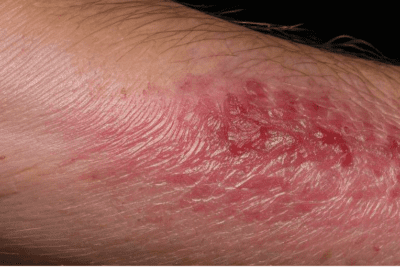
Darkened Skin Areas
Darkened patches of skin, particularly in the folds of the skin like the neck or armpits, may develop in individuals with type 2 diabetes. This condition, known as acanthosis nigricans, is often a visible indication of insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Through a combination of strategies such as weight management, healthy eating habits, physical activity, and medication, individuals can effectively control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Importance of Weight Management
Weight management plays a key role in the management of type 2 diabetes. Excess weight can contribute to insulin resistance and worsen blood sugar control. By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, individuals can improve their body's ability to utilize insulin and regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Healthy Eating Habits and Meal Planning
Adopting healthy eating habits is essential for individuals with type 2 diabetes. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall health. Meal planning and portion control are important strategies to ensure balanced nutrition and avoid spikes in blood sugar.
Incorporating Physical Activity
Physical activity is a key component of managing type 2 diabetes. Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and support weight management. Incorporating a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises into daily routines can have a positive impact on overall health.
Role of Medications and Insulin Therapy
For some individuals with type 2 diabetes, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to control blood sugar levels. In such cases, medications such as oral glucose-lowering agents or insulin therapy may be prescribed to help manage diabetes effectively. It is important to work closely with healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs.
Potential Health Complications Associated with Type 2 Diabetes
Potential health complications linked to type 2 diabetes can vary from cardiovascular issues to nerve damage, kidney problems, foot ailments, eye diseases, dental conditions, and sexual or bladder complications. These complications can significantly impact quality of life and require close monitoring and proactive management strategies to prevent further deterioration.
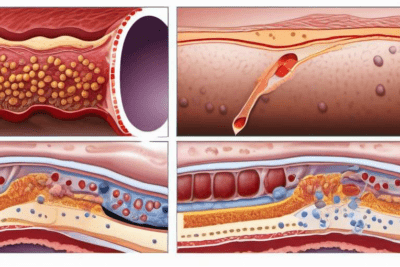
Heart Disease and Nerve Damage
- Individuals with type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk of developing heart disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues.
- Nerve damage, known as neuropathy, is another common complication that can lead to pain, numbness, tingling sensations, or loss of sensation in the extremities.
Kidney Issues and Foot Problems
- Diabetes can affect the kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy, a condition that impairs kidney function over time.
- Foot problems, such as neuropathy and poor circulation, can result in non-healing ulcers, infections, and even the need for amputation in severe cases.
Eye Diseases and Dental Conditions
- Individuals with diabetes are at higher risk of developing eye conditions like diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and cataracts, which can lead to vision impairment or blindness if left untreated.
- Dental health can also be affected, with diabetes increasing the risk of gum disease, tooth decay, and oral infections.
Sexual and Bladder Complications
- Diabetes may impact sexual function, leading to issues such as erectile dysfunction in men and decreased libido or vaginal dryness in women.
- Bladder complications can arise, including urinary incontinence, increased frequency of urination, or urinary tract infections.
Prevention Strategies for Type 2 Diabetes
Weight Loss and Physical Activity Guidelines
Weight management and regular physical activity play crucial roles in preventing type 2 diabetes. Losing excess weight reduces insulin resistance and improves blood sugar control. The American Diabetes Association recommends aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises can help increase muscle mass and further enhance glucose metabolism.
Importance of a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential for preventing type 2 diabetes. This includes following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limiting the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat snacks can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Moreover, managing stress levels through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga can also support overall well-being and metabolic health.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is key to preventing type 2 diabetes and managing its progression. Individuals at risk for diabetes should track their blood sugar levels at home using a glucometer and make necessary adjustments to their diet and lifestyle based on the results. Healthcare providers may also recommend periodic hemoglobin A1c tests to assess long-term glucose control and identify potential risk factors for diabetes development.
Early Detection and Intervention Measures
Early detection of prediabetes or diabetes can significantly impact the course of the disease. Screening tests such as fasting blood sugar, oral glucose tolerance tests, and A1c measurements can help identify individuals at risk and initiate timely interventions. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, increased physical activity, and weight loss, can delay or prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes and reduce the likelihood of complications associated with the condition.
✨ Other articles you might be interested in:



