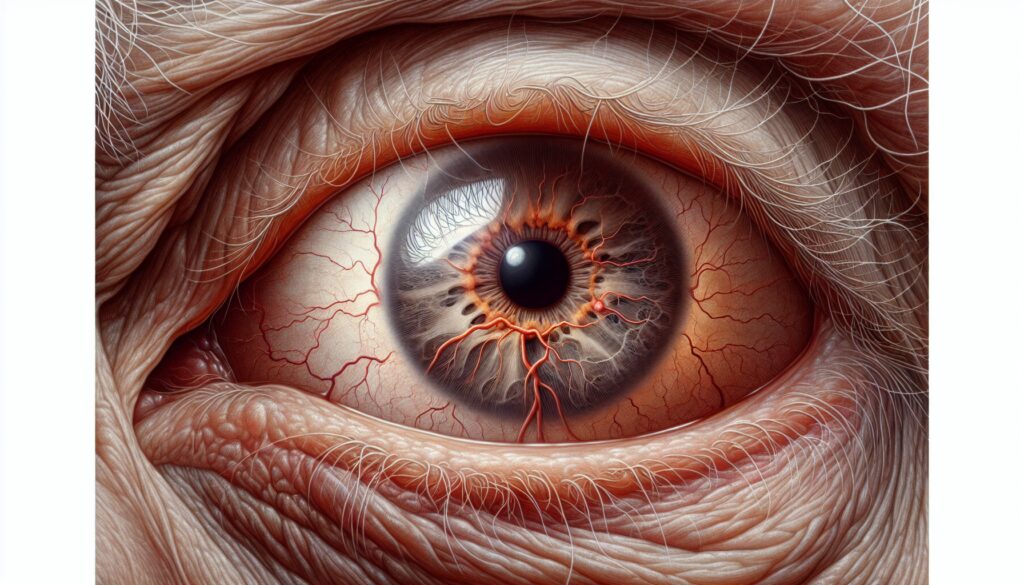
Diabetic retinopathy is a challenge for millions worldwide, and for those seeking help, the phrase "proliferative diabetic retinopathy - need help please :(" is a call for understanding and guidance. This eye condition causes significant concern due to its potential to lead to blindness if not properly managed. In this article, we'll explore the ins and outs of diabetic retinopathy, its symptoms, causes, and the options available for treatment.
🔍 Seeking a breakthrough in Type 2 Diabetes management?
Discover our expert insights and innovative approaches on ‘How to Cure Diabetes’.
Click to transform your health journey today!
What you\'ll find in this article?
- What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
- What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy?
- What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy?
- How Is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed?
- What Are the Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy?
- Can Diabetic Retinopathy Be Prevented?
- Need Help with Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy? - Exploring Treatment and Management
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the eyes. It's caused by damage to the blood vessels of the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (retina). Initially, diabetic retinopathy may cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems. However, it can eventually lead to blindness. The condition can develop in anyone who has type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The longer you have diabetes, and the less controlled your blood sugar is, the more likely you are to develop this eye complication.
Explore our specialized services in diabetes care 🌟.
From personalized diet plans to effective exercise routines, we have what you need to take control of Type 2 Diabetes.
Visit our services page now!
Among the various stages of diabetic retinopathy, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) is the most advanced stage. PDR occurs when the retina starts growing new blood vessels, a process called neovascularization. These new vessels are fragile and can leak into the vitreous, the clear gel that fills the inside of the eye, potentially leading to severe vision problems or even blindness.







What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is directly related to high blood sugar levels caused by diabetes. Over time, high sugar levels can damage the tiny blood vessels that supply the retina, leading to PDR. This damage can block blood flow, causing the retina to lack oxygen. As a result, the eye attempts to grow new blood vessels. However, these new vessels can bleed easily and cause vision problems.
Several factors can influence the development of diabetic retinopathy, including:
- Duration of diabetes – the longer you have diabetes, the greater the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- Poor control of blood sugar levels.
- High blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Pregnancy.
- Tobacco use.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Often, there are no symptoms in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy. As the condition progresses, symptoms may include:
- Spots or dark strings floating in your vision (floaters).
- Blurred vision.
- Fluctuating vision.
- Impaired color vision.
- Dark or empty areas in your vision.
- Vision loss.
It is crucial to have regular eye exams so that this condition can be caught early. If you're experiencing any signs of diabetic retinopathy, consulting a healthcare professional immediately is essential.
How Is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed?
Diabetic retinopathy is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam that includes:
- Visual acuity testing.
- Dilating the pupils to examine the retina and optic nerve.
- Conducting a tonometry test to measure the pressure inside the eye.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) to provide cross-sectional images of the retina.
Early detection is key to managing diabetic retinopathy effectively, as treatments are most successful when applied before significant damage has occurred.
What Are the Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy?
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the stage of the disease. The main goal is to slow or stop the progression of the condition. For PDR specifically, treatments may include:
- Laser surgery to shrink the abnormal blood vessels.
- Injection of corticosteroids or anti-VEGF drugs into the eye to reduce swelling and slow the growth of new blood vessels.
- Vitrectomy to remove blood from the middle of the eye.
It is important to understand your options for diabetic retinopathy treatment and work closely with your doctor to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
Can Diabetic Retinopathy Be Prevented?
While diabetic retinopathy cannot be prevented entirely, there are steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing this eye condition. Managing diabetic retinopathy effectively involves:
- Maintaining a healthy level of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
- Adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise.
- Quitting smoking or never starting.
- Having regular eye exams.
By following these steps, you can significantly lower your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy or slow its progression.
Let's take a moment to view a video that provides additional insights into the management of diabetic retinopathy.
Need Help with Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy? - Exploring Treatment and Management
How to Treat Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy?
Treating PDR involves advanced medical procedures such as laser photocoagulation and vitrectomy. Anti-VEGF injections are also used to decrease vessel growth and swelling. It's imperative to consult an ophthalmologist to discuss the best treatment plan for your condition.
It's also important to maintain stringent diabetes control to help prevent further progression of PDR. Regular monitoring and early intervention can lead to better outcomes.
Is Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy an Emergency?
If you experience sudden vision changes or vision loss, PDR may be considered an emergency. Seek immediate medical attention as timely treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
Regular eye exams can help catch PDR before it becomes an emergency, underscoring the importance of preventative care.
How Can I Help Someone with Diabetic Retinopathy?
To support someone with diabetic retinopathy, encourage them to keep their blood sugar levels under control and attend all ophthalmology appointments. Offer emotional support as coping with vision changes can be challenging.
Providing transportation to appointments and helping with medication schedules are also practical ways to assist.
Is Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy a Disability?
In some cases, PDR can lead to significant vision loss, qualifying as a disability under certain criteria. This classification helps patients receive appropriate accommodations and support services.
Individual assessment by medical professionals is necessary to determine disability status.
In conclusion, managing and treating diabetic retinopathy involves a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers. Regular eye exams, proper diabetes management, and understanding treatment options are critical to preventing vision loss. If you are or know someone struggling with "proliferative diabetic retinopathy - need help please :(", know that there is hope, and help is available. With advancements in medical treatments and a proactive approach to health, it is possible to manage diabetic retinopathy effectively.
✨ Other articles you might be interested in:
- Understanding Tresiba side effects with alcohol
- Ozempic butt: Understanding how the drug may cause your bum to vanish
- Understanding salivary gland stones in diabetics | Diabetes Forum
- Tattoos and Diabetes: Navigating Safety, Risks, and Nanotech Advances
- Teeth and diabetes forum: Caring for your dental health