The ketogenic diet, also known as the keto diet, is gaining popularity as a potential approach for managing diabetes. This low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet aims to control blood sugar levels and promote weight loss. In contrast, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. This article explores the principles, benefits, and potential risks of both diets, as well as practical tips for incorporating them into a diabetes management plan. Before making any dietary changes, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it is appropriate for individual needs and goals.
- Understanding the Ketogenic Diet - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
- The Role of the Mediterranean Diet in Diabetes Management - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
- A Comparison of Keto Diet and Mediterranean Diet - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
- Considerations for People with Diabetes - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
- Practical Tips for Incorporating Keto Diet or Mediterranean Diet - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
Exploring the fundamentals of the ketogenic diet is crucial for individuals considering it as a potential approach to diabetes management. This section provides an overview of how the ketogenic diet works, its health benefits, and the existing clinical trials and research supporting its efficacy.
How the Ketogenic Diet Works
The ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat eating plan that aims to shift the body's metabolic state into ketosis. By severely restricting carbohydrate intake, typically to less than 50 grams per day, the body transitions into a state where it primarily utilizes ketones, derived from fats, as a source of energy instead of glucose from carbohydrates.
This shift in fuel utilization leads to an increase in ketone production and a decrease in blood glucose levels. The body enters a state of metabolic flexibility, wherein it becomes efficient at burning stored fat for energy, including excess body fat, potentially aiding in weight loss.
Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet has shown promise in various health aspects beyond weight loss. Research suggests that it may improve insulin sensitivity, facilitate better blood sugar control, and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, it may help lower triglyceride levels, increase levels of HDL (good) cholesterol, and promote overall cardiovascular health.
Additionally, the ketogenic diet has been explored for its potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, showing promise in conditions such as epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and certain types of cancer.
Clinical Trials and Research on the Ketogenic Diet
A growing body of research supports the use of the ketogenic diet for managing diabetes and improving metabolic health. Several clinical trials have demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity, and promoting weight loss in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Furthermore, studies have shown that the ketogenic diet may enhance glycemic control and reduce the need for diabetes medications in people with type 2 diabetes. It is worth noting that individual responses to the diet may vary, and consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for personalized guidance and monitoring.
In conclusion, understanding the ketogenic diet involves grasping its underlying mechanisms, recognizing its potential health benefits, and being aware of the existing clinical trials and research supporting its use. With this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions regarding its suitability as part of their diabetes management strategy.
The Role of the Mediterranean Diet in Diabetes Management - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
The Mediterranean diet has gained recognition for its potential benefits in managing diabetes. This section explores the key aspects of the Mediterranean diet and how it can be incorporated into diabetes care.

Exploring the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is inspired by traditional dietary patterns in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece and Italy. It emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, including:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Legumes
- Healthy fats, like olive oil and nuts
- Lean sources of protein, such as fish and poultry
- Minimally processed dairy products, like yogurt and cheese
This eating pattern also encourages moderate consumption of red wine with meals, although this aspect should be approached with caution for individuals with certain health conditions or if alcohol is contraindicated.
Incorporating Mediterranean Diet for Diabetes Care
The Mediterranean diet offers several potential benefits for individuals with diabetes. It is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which may help support overall health and glycemic control.
Meal Planning and Food Choices
When incorporating the Mediterranean diet into diabetes care, focus on the following:
- Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into meals and snacks
- Choose whole grains over refined grains, such as whole wheat, quinoa, and brown rice
- Include legumes, such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans, as plant-based sources of protein and fiber
- Opt for healthy fats like olive oil, avocados, and nuts in moderation
- Select lean sources of protein, such as fish, poultry, and tofu
- Moderate consumption of red wine, if appropriate and permitted by your healthcare provider
Addressing Nutritional Needs
While the Mediterranean diet offers numerous health benefits, it is essential to pay attention to any nutritional deficiencies that may arise. Some individuals may need additional supplements, such as vitamin B12 or omega-3 fatty acids, particularly if they include limited fish or dairy products in their diet.
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, along with consultation with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian, is crucial to tailor the Mediterranean diet to individual needs and ensure proper management of diabetes.Note: This text is written specifically for the designated section and does not include information from other parts of the index.
A Comparison of Keto Diet and Mediterranean Diet - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
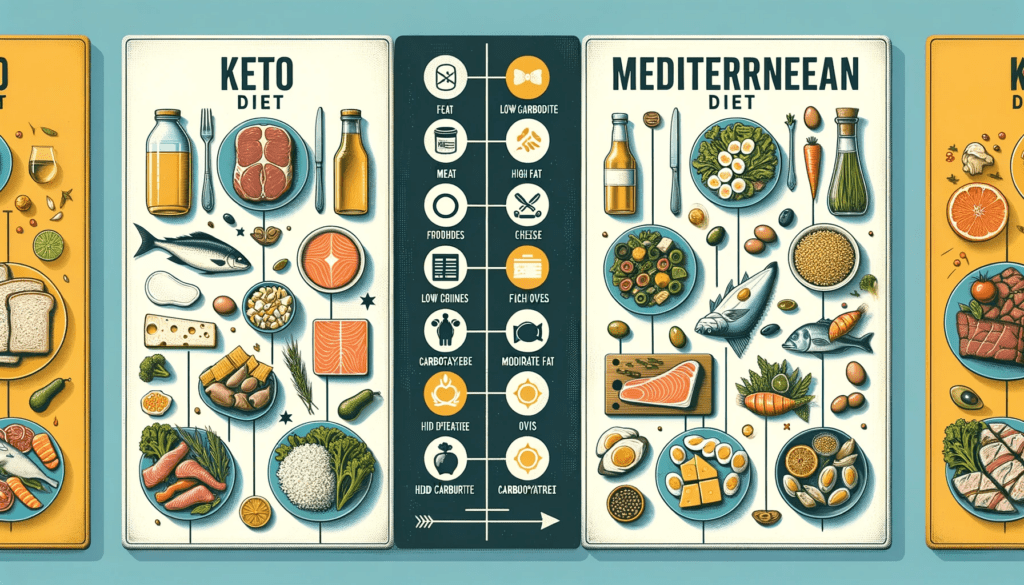
In this section, we will explore the key differences in principles and approaches between the keto diet and the Mediterranean diet, as well as their effects on blood glucose levels and weight loss.
Contrasting Principles and Approaches
The keto diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that aims to induce a state of ketosis in the body. It emphasizes consuming foods high in fats, moderate in protein, and very low in carbohydrates. The Mediterranean diet, on the other hand, is characterized by a balanced approach, focusing on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, fish, and healthy fats like olive oil. It is moderate in carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- The keto diet severely restricts carbohydrate intake to achieve ketosis, while the Mediterranean diet allows for a moderate consumption of carbohydrates.
- The keto diet promotes a higher intake of saturated fats from animal sources, while the Mediterranean diet encourages the consumption of unsaturated fats like olive oil and fatty fish.
- Unlike the keto diet, the Mediterranean diet includes a variety of food groups to ensure a well-rounded nutrient intake.
Effects on Blood Glucose Levels and Weight Loss
Both the keto diet and the Mediterranean diet have shown potential benefits for managing blood glucose levels and promoting weight loss, although their mechanisms differ.
Studies have suggested that the keto diet can lead to rapid weight loss and improved glycemic control in the short term, primarily due to the significant reduction in carbohydrate intake. By restricting carbohydrates, the body's reliance on glucose decreases, and it starts utilizing ketones for energy.
The Mediterranean diet, with its emphasis on whole foods and a moderate carbohydrate intake, has also demonstrated positive effects on blood glucose control and weight management. It provides a balanced approach to nutrition, ensuring a steady release of glucose into the bloodstream and promoting satiety through its fiber-rich components.
While both diets can lead to weight loss and improved blood glucose control, it is important to consider long-term sustainability and individual preferences when choosing a dietary approach.
Overall, understanding the principles and effects of the keto diet and Mediterranean diet can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about which dietary approach may be most suitable for their needs and goals.
Considerations for People with Diabetes - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
When it comes to managing diabetes, there are important considerations to keep in mind before starting any dietary changes, including the ketogenic diet. It is vital to consult with your healthcare provider to ensure that any modifications align with your specific needs and goals.
Consulting with Your Healthcare Provider
Prior to embarking on a ketogenic diet or any other dietary regimen, it is recommended to seek guidance from your healthcare provider, particularly if you have diabetes. Your healthcare provider can assess your medical history, medications, and individual circumstances to determine the potential benefits and risks associated with the ketogenic diet.
Managing Glucose Levels and Medication
One critical aspect of diabetes management is the regulation of blood glucose levels. As you embark on a ketogenic diet, it is crucial to monitor your blood glucose levels regularly and work closely with your healthcare provider to adjust your medication or insulin if necessary. Close monitoring will help optimize your glucose control and ensure safety while on the ketogenic diet.
Potential Benefits and Risks of the Keto Diet
Ketogenic diet may improve glucose control, weight management, and reduce medication or insulin dependence in diabetes patients. However, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks and challenges that come with this diet.
- Ketogenic diet risk: potential hypoglycemia due to drastic carbohydrate reduction causing lower blood sugar levels. This risk reinforces the importance of closely monitoring glucose levels and adjusting medication accordingly in consultation with your healthcare provider.
- Another consideration is the difficulty of long-term adherence to the ketogenic diet. Sustaining a restrictive eating plan can be challenging, possibly affecting the maintenance of desired health outcomes.
- Additionally, the ketogenic diet may result in nutritional deficiencies if not carefully planned. Restricting carbohydrates could limit access to vital nutrients found in fruits, whole grains, and certain vegetables. It is crucial to work with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
Consider the ketogenic diet’s benefits for diabetes management, weighing potential risks and challenges carefully. Seek guidance from your healthcare provider and consider an individualized approach that aligns with your specific needs, goals, and lifestyle.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Keto Diet or Mediterranean Diet - Keto Diet and Diabetes: Ultimate Guide to Manage Type 2
Meal Planning and Food Choices
When incorporating the keto diet or Mediterranean diet for diabetes management, it is important to plan your meals thoughtfully. Focus on low-carb, high-fat for keto, and whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats for the Mediterranean diet. Consider the following tips:
- Select lean sources of protein, such as fish, poultry, and tofu.
- Incorporate a variety of colorful vegetables into your meals.
- Include healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocado, and nuts.
- Avoid processed foods and added sugars.
- Experiment with different herbs and spices to add flavor to your dishes.
Addressing Nutritional Needs
Both the keto diet and Mediterranean diet can provide adequate nutrition when followed properly. However, it is essential to ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs while managing diabetes. Consider the following:
- Monitor your intake of essential vitamins and minerals, and consider supplementation if necessary.
- Consult with a registered dietitian to create a balanced and personalized meal plan.
- Incorporate a variety of nutrient-dense foods to ensure a well-rounded diet.
Establishing a Sustainable Diet Routine
Maintaining a long-term diet routine is crucial for successful diabetes management. Consider the following tips to establish a sustainable routine:
- Gradually transition into the desired diet plan to make the adjustment process easier.
- Find support from friends, family, or diabetes support groups to stay motivated.
- Include physical activity as a part of your routine to enhance the overall benefits.
- Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly and make adjustments as needed in consultation with your healthcare provider.
- Set realistic goals and celebrate small milestones along the way to stay motivated.
Incorporate keto or Mediterranean diets for diabetes with careful planning, attention to nutrition, and a sustainable routine commitment. Follow these tips to optimize diet benefits for better glucose control and overall well-being.
Disclaimer: Consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your diet or diabetes management routine.