Understanding diabetes and its various types is crucial for effective management and treatment. If you're wondering "Which Type of Diabetes Do I Have?", it's important to recognize the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes, the symptoms they share, and the distinct approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
🔍 Seeking a breakthrough in Type 2 Diabetes management?
Discover our expert insights and innovative approaches on ‘How to Cure Diabetes’.
Click to transform your health journey today!
What you\'ll find in this article?
- What Are The Main Differences Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
- What Are The Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
- How Is Type 1 Different From Type 2 Diabetes In Diagnosis?
- What Factors Contribute To Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
- Can Type 1 Or Type 2 Diabetes Be Prevented?
- What Treatments Are Available For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
- Deepening Your Understanding: Questions Related to Diabetes Types
What Are The Main Differences Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that typically manifests in childhood or adolescence. Your immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to a lack of insulin.
On the other hand, Type 2 Diabetes develops primarily in adults and is often associated with lifestyle factors. It is characterized by insulin resistance, where your body produces insulin but does not use it effectively.
In both conditions, the lack of effective insulin function leads to high blood sugar levels, which can cause a range of health issues if not managed properly.




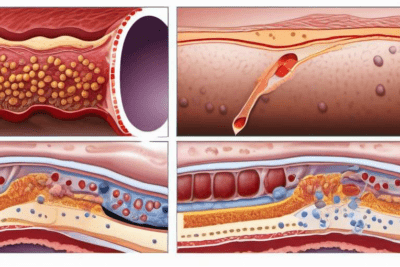
Explore our specialized services in diabetes care 🌟.
From personalized diet plans to effective exercise routines, we have what you need to take control of Type 2 Diabetes.
Visit our services page now!
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
Both types of diabetes share common signs, including excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. However, Type 1 Diabetes symptoms can develop swiftly and become more severe quickly.
Patients with Type 2 Diabetes might experience symptoms like blurred vision, slow-healing sores, and darkened areas of the skin, particularly in the neck and armpits, indicating insulin resistance.
Recognizing these symptoms is vital, as early detection leads to more effective management of the disease.
How Is Type 1 Different From Type 2 Diabetes In Diagnosis?
Diagnosing diabetes typically involves blood tests such as the A1C test, which measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, and the glucose tolerance test.
For Type 1 Diabetes, specific antibody tests are important for accurate diagnosis as they can identify the autoimmune nature of the disease.
Understanding the specific type through these diagnostic tests is essential for the correct treatment strategy.
What Factors Contribute To Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes is often linked to genetic factors and can occur in individuals with a family history of the condition.
For Type 2 Diabetes, factors such as obesity, poor diet, and physical inactivity significantly contribute to its development. Age and genetics also play a role.
Identifying these risk factors can help with prevention and management efforts.
Can Type 1 Or Type 2 Diabetes Be Prevented?
Currently, there's no known way to prevent Type 1 Diabetes. However, adopting a healthy lifestyle can prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 Diabetes.
Prevention strategies include maintaining a healthy weight, regular physical activity, and a balanced diet. Monitoring your blood sugar levels is also crucial.
While you can't always prevent diabetes, understanding and managing risk factors can significantly reduce its impact.
What Treatments Are Available For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes management requires lifelong insulin therapy. Patients may need multiple daily injections or use an insulin pump.
Type 2 Diabetes management often starts with lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise. If these are insufficient, medications or insulin therapy may become necessary.
Staying informed about the latest treatment options and working closely with healthcare providers is key.
How Do You Know If It's Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes?
The presence of certain symptoms and the results of antibody tests can help determine if it's Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes. A sudden onset of severe symptoms often indicates Type 1.
For a definitive diagnosis, consult a healthcare provider who can administer the appropriate tests and provide an accurate diagnosis.
Which Is More Common, Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 Diabetes is significantly more common than Type 1, with lifestyle factors contributing to its higher prevalence.
Understanding the prevalence can inform healthcare strategies and personal awareness for early detection and management.
How Do I Know If I Have Diabetes Type 1?
If you are experiencing rapid onset of severe symptoms such as drastic weight loss, extreme thirst, and frequent urination, you might have Type 1 Diabetes.
Seek immediate medical attention for blood tests that can confirm the type of diabetes.
What Blood Tests Differentiate Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
Blood tests such as the A1C test and glucose tolerance test are used for initial diagnosis. Specific antibody tests can differentiate Type 1 from Type 2.
Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial for conducting and interpreting these tests correctly.
To further your understanding, let's look at a relevant video that elaborates on diabetes management strategies and provides useful insights.
In summary, distinguishing between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes is key for effective management. Recognizing early symptoms and understanding the factors that contribute to each type can lead to a timely and accurate diagnosis. Whether it's through lifestyle changes, medication, or insulin therapy, proper treatment is available to manage diabetes effectively. Stay informed and consult with healthcare professionals to navigate the complexities of this condition.
✨ Other articles you might be interested in:



