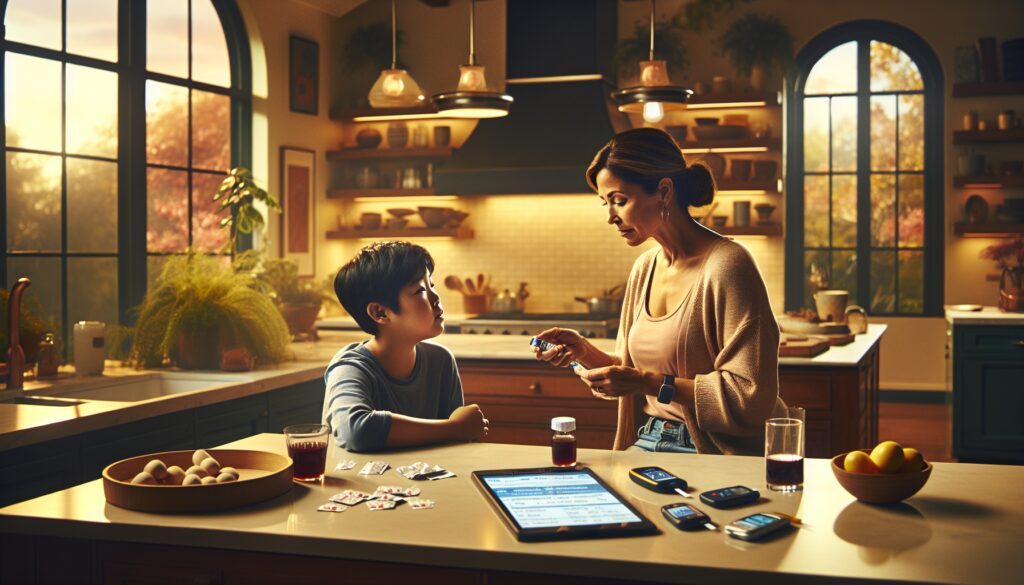
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood glucose, can become an alarming condition if not addressed promptly. This article will offer essential insights into recognizing and managing hypoglycemia effectively, including an emergency care plan and treatment guidelines.
🔍 Seeking a breakthrough in Type 2 Diabetes management?
Discover our expert insights and innovative approaches on ‘How to Cure Diabetes’.
Click to transform your health journey today!
What you\'ll find in this article?
What Are the Symptoms of Hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia symptoms can range from mild to severe. Common signs include shaking, sweating, and a feeling of weakness. As the condition progresses, individuals may experience dizziness, confusion, and difficulty speaking. Severe hypoglycemia can lead to more daunting symptoms such as blurred vision, seizures, and even loss of consciousness.
It's crucial to recognize these symptoms early as prompt treatment is necessary to prevent complications. For those with diabetes, hypoglycemia is often a side effect of insulin therapy, and monitoring blood glucose levels can help mitigate risks.
Understanding these indicators is paramount for both diabetics and caregivers to ensure timely intervention and avert potential emergencies.
Explore our specialized services in diabetes care 🌟.
From personalized diet plans to effective exercise routines, we have what you need to take control of Type 2 Diabetes.
Visit our services page now!











How to Treat Hypoglycemia in an Emergency
When encountering an episode of hypoglycemia, the initial step is to check the blood glucose level. If it's below 70 mg/dL, consuming 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or juice, is recommended.
After 15 minutes, rechecking blood glucose levels is essential to ensure they are rising. If they remain low, the process should be repeated until levels normalize. For unconscious individuals or those unable to swallow, emergency services should be contacted immediately.
Family members and caregivers should be trained to administer glucagon injections in severe cases when the individual is unable to take sugar orally.
What Is the Nursing Care Plan for Hypoglycemia?
Nurses play a vital role in managing hypoglycemia, particularly in hospital or long-term care settings. The nursing care plan includes routine monitoring of blood glucose levels, administering insulin correctly, and providing patient education on managing their condition.
It also involves dietary planning to ensure balanced carbohydrate intake throughout the day and recognizing early signs of hypoglycemia. Nurses must also be ready to intervene with fast-acting carbohydrates or glucagon as needed.
Education on lifestyle modifications, like consistent meal timings and avoiding excessive alcohol, is also a critical component of the care plan.
Hypoglycemia Treatment Guidelines
The cornerstone of hypoglycemia treatment is to consume fast-acting carbohydrates immediately upon experiencing symptoms. Long-term management involves balancing insulin doses, meal plans, and physical activity.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems can be invaluable for patients with frequent episodes of hypoglycemia or hypoglycemia unawareness. They provide real-time glucose readings and alerts before levels become too low.
Structured patient education programs can significantly reduce hypoglycemia risk by helping individuals understand their treatment plan and how different factors affect their blood glucose.
How to Manage Neonatal Hypoglycemia
Neonatal hypoglycemia requires prompt treatment to prevent neurological damage. Initial management involves feeding with formula or breast milk to raise blood glucose levels.
If feeding doesn't normalize glucose levels, intravenous glucose may be necessary. Continuous monitoring of blood glucose is crucial for infants at risk, such as those born to diabetic mothers or with low birth weights.
Healthcare providers should also educate parents about signs of hypoglycemia and proper feeding techniques to prevent recurrence.
What Is Hypoglycemia Unawareness?
Hypoglycemia unawareness is a condition where the individual does not experience the typical warning symptoms of low blood glucose. This can lead to a higher risk of severe hypoglycemia as the person may not realize they need to take corrective action.
Management strategies include raising the blood glucose targets to help restore some symptom awareness and using CGM with alert features. It's also essential for individuals with hypoglycemia unawareness to have a strong support network that can assist in case of an emergency.
What Is the Nursing Care Plan for Hypoglycemia?
A nursing care plan for hypoglycemia involves regular monitoring of glucose levels, administering medication as prescribed, and providing patient education on lifestyle adjustments to prevent episodes.
Nurses should also be adept at recognizing early signs of hypoglycemia and ready to administer treatment such as fast-acting carbohydrates or glucagon injections.
What Is the Emergency Response to Low Blood Sugar?
An emergency response to low blood sugar involves immediate consumption of fast-acting carbohydrates and rechecking glucose levels after 15 minutes. If the patient is unresponsive or unable to take oral carbohydrates, emergency medical services should be contacted for potential glucagon administration.
Emergencies can strike without warning, as illustrated in this video, which provides a comprehensive look at hypoglycemia response.
What Is the EMS Protocol for Hypoglycemia?
The EMS protocol dictates that emergency medical personnel should assess the patient's airway, breathing, and circulation, and check blood glucose levels. If hypoglycemia is confirmed and the patient can swallow, oral glucose should be provided.
If the patient is unconscious, glucagon may be administered intramuscularly or intravenously. Transport to a medical facility for further care is often necessary.
What Is the Emergency Management of Hypoglycemia in Diabetes?
Emergency management for diabetics experiencing hypoglycemia includes the immediate consumption of 15-20 grams of carbohydrates. If there is no improvement, repeating the process is advised.
Patient education on the proper administration of insulin and meal planning is critical to prevent future hypoglycemia episodes.
In conclusion, managing hypoglycemia effectively requires a combination of immediate treatment, ongoing management, education, and support. By understanding the symptoms and having an emergency care plan in place, individuals at risk and their caregivers can take vital steps to ensure safety and well-being.
✨ Other articles you might be interested in:
- Understanding diabetes and emotional health challenges
- Understanding the Mental Toll of Diabetes on Everyday Life
- Understanding the Differences: Ophthalmologist, Optometrist, Retina Specialist? What's the Difference?
- Understanding serious foot problems and diabetes
- Understanding diabetes and foot problems



