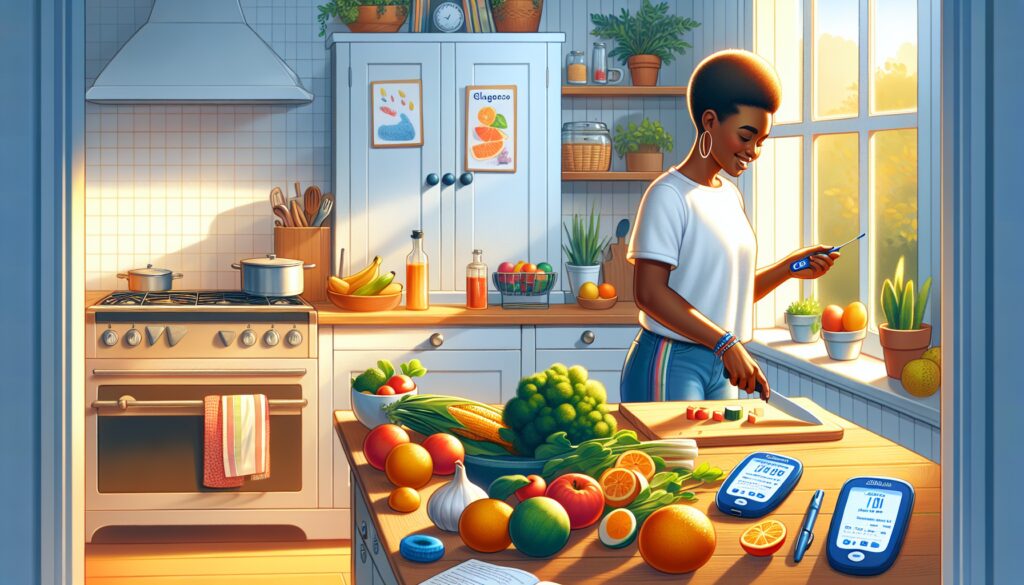
Managing Type 1 diabetes involves a comprehensive understanding of the condition and a proactive approach to self-care. It requires regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to a balanced diet, physical activity, and collaboration with a healthcare team. With the right strategies, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
🔍 Seeking a breakthrough in Type 2 Diabetes management?
Discover our expert insights and innovative approaches on ‘How to Cure Diabetes’.
Click to transform your health journey today!
What you\'ll find in this article?
What Are the Basics of Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This leads to a lack of insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood glucose levels. Understanding the basics of this condition is the first step in the journey of self-care.
Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of Type 1 diabetes management, as people with the condition require daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump. Additionally, regular blood glucose monitoring is essential to keep levels within a target range.
Recognizing the signs of both high and low blood glucose is vital for immediate treatment. High blood glucose, known as hyperglycemia, can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Conversely, low blood glucose, or hypoglycemia, can be equally dangerous and requires quick action to bring levels back to normal.
Explore our specialized services in diabetes care 🌟.
From personalized diet plans to effective exercise routines, we have what you need to take control of Type 2 Diabetes.
Visit our services page now!





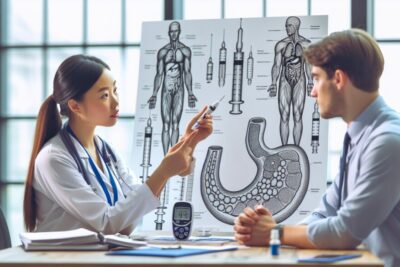

How to Manage Blood Glucose Levels Effectively
Effective management of blood glucose levels is fundamental for those with Type 1 diabetes. This includes routine blood glucose monitoring, understanding how different foods affect blood sugar, and recognizing the impact of stress and physical activity on glucose levels.
People with Type 1 diabetes should work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best insulin therapy plan. Insulin dosages must be adjusted according to food intake, activity levels, and current blood glucose readings.
Technological advancements such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) have made it easier to track blood glucose levels in real-time, providing valuable data that can help refine diabetes management strategies.
What Does a Diabetes Care Team Do?
A diabetes care team is a group of healthcare professionals who specialize in diabetes management. The team typically includes an endocrinologist, diabetes educator, dietitian, and a primary care physician.
The care team works collaboratively with the patient to create a personalized diabetes management plan. They provide education on insulin usage, diet, exercise, and how to handle emergency situations like hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis.
Regular appointments with the diabetes care team are crucial for monitoring the progress of diabetes management and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Importance of Nutrition and Physical Activity
A balanced diet and regular physical activity are key components of Type 1 diabetes management. Carbohydrate counting is a technique often recommended to help individuals plan their meals and determine insulin dosages accurately.
Physical activity not only promotes cardiovascular health but also improves insulin sensitivity. It's important for individuals with Type 1 diabetes to monitor their blood glucose levels before, during, and after exercise to prevent hypoglycemia.
Working with a dietitian can be incredibly helpful in creating a meal plan that considers individual preferences, nutritional needs, and the complexities of managing blood glucose levels.
Understanding Diabetes Complications
Long-term complications of Type 1 diabetes may affect various organs in the body, including the heart, kidneys, nerves, and eyes. Keeping blood glucose levels within the recommended range can help prevent or delay these complications.
Regular screenings and check-ups are essential for early detection and treatment of potential complications. This may include annual eye examinations, kidney function tests, and cardiovascular assessments.
By staying informed and vigilant, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can take proactive steps to maintain their health and reduce the risk of complications.
Special Considerations for Different Age Groups
Managing Type 1 diabetes requires tailored approaches for different age groups. Children, adolescents, adults, and seniors all have unique needs when it comes to diabetes care.
For children and adolescents, factors like growth, puberty, and emotional well-being play a significant role in diabetes management. Parents and caregivers need to be actively involved in their child's daily care.
Adults may need to balance diabetes management with work, family, and other responsibilities. Meanwhile, seniors may face challenges such as decreased mobility or the presence of other health conditions.
What is Type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease characterized by the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Without insulin, the body cannot regulate blood glucose levels effectively.
Those afflicted with Type 1 diabetes must rely on exogenous insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels and prevent the acute and chronic complications of the disease.
How do you manage Type 1 diabetes?
Management of Type 1 diabetes involves a multi-faceted approach including regular monitoring of blood glucose, insulin therapy, dietary adjustments, and physical activity.
It also includes education about the condition and how to react to blood glucose variations, as well as regular consultations with a diabetes care team.
What is the role of a diabetes care team?
The role of a diabetes care team is to provide comprehensive care and support to individuals with Type 1 diabetes. This includes education, medical management, and emotional support.
They also assist with the fine-tuning of insulin therapy and the implementation of lifestyle changes that can improve blood glucose control and overall health.
Can diet and exercise help manage Type 1 diabetes?
Yes, diet and exercise are critical elements of managing Type 1 diabetes. Healthy eating habits help maintain steady blood glucose levels, while regular exercise can increase insulin sensitivity.
Both should be tailored to the individual's needs, preferences, and diabetes management goals.
What are the complications of Type 1 diabetes?
Complications of Type 1 diabetes can be severe and include cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, and an increased risk of infections.
However, with optimal blood glucose control and regular medical follow-up, the risk and progression of these complications can be significantly reduced.
To explore these concepts further, here is a video discussing insights into managing Type 1 diabetes:
In conclusion, effective self-care for Type 1 diabetes involves a committed approach to monitoring and management. With the right support and resources, individuals can navigate their condition successfully and enjoy a high quality of life.
✨ Other articles you might be interested in:



