In 2023, significant progress has been made in finding a cure for type 1 diabetes. Islet cells play a crucial role in this disease, and researchers believe they are destroyed due to autoimmune attacks. Transplanting islet cells is a promising alternative treatment option, as it restores the necessary beta cells responsible for insulin production. Neovascularization and exploring new transplantation sites are being studied to ensure the survival of transplanted cells. Moreover, scientists are investigating alternative sources of beta cells and exploring immunotherapies to modulate the immune response. Technological advancements and gene therapy also show promise in managing and curing type 1 diabetes.
- Overview of Type 1 Diabetes Cure in 2023
- Understanding the Role of Islet Cells in Type 1 Diabetes
- Advances in Transplanting Islet Cells for Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
- Neovascularization and Alternative Transplantation Sites for Islet Cells
- Exploring Alternative Sources of Beta Cells for Type 1 Diabetes Cure
- Immunotherapies and Modulating the Immune Response in Type 1 Diabetes
- Technological Advances in Type 1 Diabetes Management
- Investigating Gene Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes Cure
Overview of Type 1 Diabetes Cure in 2023
In 2023, significant advancements have been made in the search for a cure for type 1 diabetes. Researchers are focused on understanding the role of islet cells in this disease, which are believed to be destroyed by autoimmune attacks. Islet cells are a vital component of the pancreas, producing hormones like insulin.
Transplanting islet cells has emerged as a promising treatment option. Rather than a full pancreas transplant, islet cell transplantation aims to restore the necessary beta cells responsible for insulin production. This approach offers technical advantages and reduces the risk of complications. However, immunosuppression is required to prevent host rejection.
Neovascularization, the formation of new blood vessels, is crucial for the survival of transplanted islet cells. Scientists are researching alternative transplantation sites that provide better microenvironments, exploring the encapsulation of islet cells, developing immunosuppression methods without CNIs, and investigating biomarkers for islet damage.
Additionally, the field of regenerative medicine offers hope for the future. Alternative sources of beta cells, such as adult stem cells or progenitor cells, could overcome the shortage of organ donors. The ability of alpha cells to spontaneously transform into beta cells in healthy and diabetic pancreatic islets also holds potential for beta cell regeneration.
These approaches, combined with safe immunological interventions, present a promising path toward an effective cure for type 1 diabetes in the near future.
Understanding the Role of Islet Cells in Type 1 Diabetes
Islet cells play a crucial role in type 1 diabetes, as they are responsible for producing important hormones like insulin. These cells are found in small clusters within the pancreas known as the pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans.
The beta cells within the islets are specifically responsible for the production and release of insulin into the bloodstream. In type 1 diabetes, these beta cells are mistakenly attacked and destroyed by the immune system, leading to an insufficient supply of insulin.
This destruction of beta cells results in elevated blood sugar levels, as insulin is necessary for the regulation and uptake of glucose by cells for energy. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot enter cells effectively, leading to a buildup in the bloodstream.
Understanding the role of islet cells in type 1 diabetes is crucial for developing effective treatments and potential cures. Researchers are exploring different approaches, such as islet cell transplantation or the use of alternative sources like stem cells, to restore the functions of beta cells and improve insulin production.
By delving deeper into the mechanisms behind the destruction of islet cells and finding ways to protect or regenerate them, we can pave the way towards a future where type 1 diabetes can be effectively managed or cured.
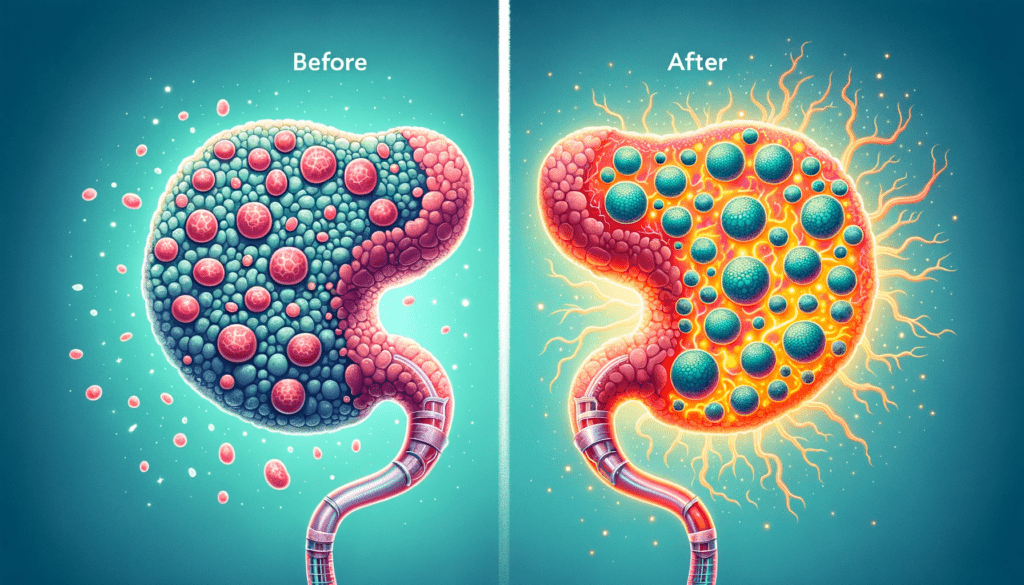
Advances in Transplanting Islet Cells for Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
Transplanting islet cells has emerged as a promising approach for treating type 1 diabetes. Instead of a full pancreas transplant or an artificial pancreas, islet cell transplantation focuses on restoring the necessary beta cells responsible for insulin production. This technique offers technical advantages and reduces the risk of complications.
Islet transplantation requires immunosuppression to prevent host rejection. Additionally, neovascularization, the formation of new blood vessels, is crucial for the survival of transplanted islet cells. Researchers are investigating alternative transplantation sites that provide a better microenvironment, as well as the encapsulation of islet cells, immune-suppression without CNIs, biomarkers for islet damage, and the scarcity of islet donors.
Furthermore, seeking alternative sources of beta cells, such as adult stem cells or progenitor cells, holds the potential to overcome the shortage of organ donors. The field of regenerative medicine provides hope for the near future, but a combination of safe immunological interventions and beta cell regeneration approaches will be required for an effective cure for type 1 diabetes. Additionally, the spontaneous conversion and transdifferentiation of alpha cells into beta cells in both healthy and diabetic pancreatic islets offer a potential future source for beta cell regeneration.
Neovascularization and Alternative Transplantation Sites for Islet Cells
Neovascularization, the formation of new blood vessels, plays a crucial role in the successful transplantation of islet cells for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Researchers are investigating alternative transplantation sites that offer a better microenvironment for the survival and functioning of transplanted islet cells. By exploring these options, they aim to improve the long-term outcomes of islet cell transplantation.
Studies are being conducted to identify sites that provide a significant blood supply to the transplanted islet cells, enhancing their survival and functionality. Furthermore, researchers are exploring the encapsulation of islet cells as a protective barrier against the immune system, reducing the need for immunosuppression therapy and improving long-term graft survival.
The scarcity of islet cell donors remains a challenge. However, advancements in regenerative medicine hold promise for overcoming this limitation. Alternative sources of beta cells, such as adult stem cells or progenitor cells, offer potential solutions for addressing the shortage of donor organs. Researchers are working towards safely combining immunological interventions with beta cell regeneration approaches to achieve an effective cure for type 1 diabetes.
Overall, ongoing research is focused on optimizing the transplantation process, improving neovascularization at alternative sites, and exploring alternative sources of beta cells, aiming towards an effective cure for type 1 diabetes in the year 2023.

Exploring Alternative Sources of Beta Cells for Type 1 Diabetes Cure
Researchers are investigating promising alternatives to address the scarcity of organ donors in the quest for a cure for type 1 diabetes. One potential solution lies in the use of adult stem cells and progenitor cells as an alternative source of beta cells. The field of regenerative medicine holds hope for the near future, as these cells could potentially overcome the limitations associated with organ donation.
Another avenue of exploration lies in the spontaneous change and transdifferentiation of alpha cells into beta cells within healthy and diabetic pancreatic islets. This remarkable finding offers a potential source for beta cell regeneration, further advancing the prospects of finding an effective cure.
By combining safe immunological interventions with beta cell regeneration approaches, researchers aim to achieve an effective cure for type 1 diabetes. The supply of beta cells is essential, and finding alternative sources may significantly contribute towards this goal.
- Investigation of adult stem cells and progenitor cells as alternative sources of beta cells
- Exploration of spontaneous transdifferentiation of alpha cells into beta cells within pancreatic islets
- Potential for beta cell regeneration to overcome organ donor scarcity
These ongoing efforts in exploring alternative sources of beta cells bring us closer to finding a viable cure for type 1 diabetes, offering a future where individuals with this condition can lead healthier lives without the reliance on external insulin administration.
Immunotherapies and Modulating the Immune Response in Type 1 Diabetes
Researchers explore immunotherapies' potential to modulate immune responses in pursuit of a 2023 type 1 diabetes cure. Therapies targeting the autoimmune attack on beta cells aim to prevent destruction of insulin-producing cells.
One avenue of exploration involves the use of immune checkpoints to restore immune system balance. Inhibiting molecules like PD-1 or CTLA-4 may prevent autoimmune destruction, preserving beta cell function. This approach shows promise in preclinical studies and may offer a new direction for type 1 diabetes treatment.
Using biologics like monoclonal antibodies to target specific immune cells or modulate activity is another approach. Targeting T lymphocytes with anti-CD3 antibodies has helped preserve beta cell function in some with type 1 diabetes.
Furthermore, the development of antigen-specific immunotherapies aims to redirect the immune system's response specifically against harmful autoantigens. Researchers are exploring vaccines and other immunomodulatory approaches to induce tolerance to the beta cells and prevent further attack.
Immunotherapies may modulate immune response in type 1 diabetes, possibly halting or slowing disease progression. Ongoing research and trials promise improved treatments and a potential cure for type 1 diabetes soon.
Technological Advances in Type 1 Diabetes Management
2023’s tech advancements revolutionized type 1 diabetes management, offering innovative solutions for affected individuals. Advancements improve glucose monitoring and insulin administration, enhancing blood sugar control and quality of life.
Some of the key technological advances include:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: These devices offer real-time glucose readings, enabling continuous blood sugar level tracking. It helps in making informed decisions regarding insulin dosing and dietary adjustments.
- Insulin Pumps: These wearable devices deliver insulin automatically, eliminating the need for multiple daily injections. They provide precise and customized insulin delivery based on individual needs.
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: Closed-loop systems combine CGM and insulin pump technology, mimicking a healthy pancreas. They continuously monitor glucose levels and adjust insulin delivery accordingly, providing optimal glycemic control.
- Smart Insulin Pens: Pens sync with apps for tracking insulin, setting reminders, and monitoring diabetes trends. They simplify insulin administration and enhance adherence to treatment plans.
Technological advancements allow better control and improved health for individuals with type 1 diabetes. Advancing technology promises further innovations for enhanced management and treatment of type 1 diabetes.
Investigating Gene Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes Cure
Gene therapy is emerging as a promising approach in the pursuit of a cure for type 1 diabetes in 2023. Researchers explore reprogramming cells to produce insulin, compensating for lost beta cells. Scientists aim to restore insulin production and reduce dependence on external insulin by introducing specific genes into cells.
Continual advancements in gene therapy techniques provide renewed hope for individuals living with type 1 diabetes. Through intricate genetic engineering and targeted delivery methods, researchers are striving to overcome the autoimmune destruction of beta cells. The objective is to reset the body's immune response, effectively protecting the newly reprogrammed cells, and enabling long-term insulin production.
While gene therapy is still in its investigational stage, preliminary results from animal studies and early human trials are encouraging. However, comprehensive research and rigorous testing are necessary to ensure the therapy's safety, efficacy, and long-term sustainability.
Gene therapy may offer a permanent solution to Type 1 diabetes by restoring natural insulin production. Scientists unraveling gene manipulation, foresee gene therapy as a transformative approach in pursuing a diabetes cure.
Stay informed on gene therapy's potential to revolutionize type 1 diabetes treatment.
- Investigate reprogramming other cells to produce insulin
- Striving to reset the body's immune response
- Targeted delivery methods for gene therapy
- Ensuring safety, efficacy, and long-term sustainability
- Exploring the potential of gene therapy for a long-lasting cure