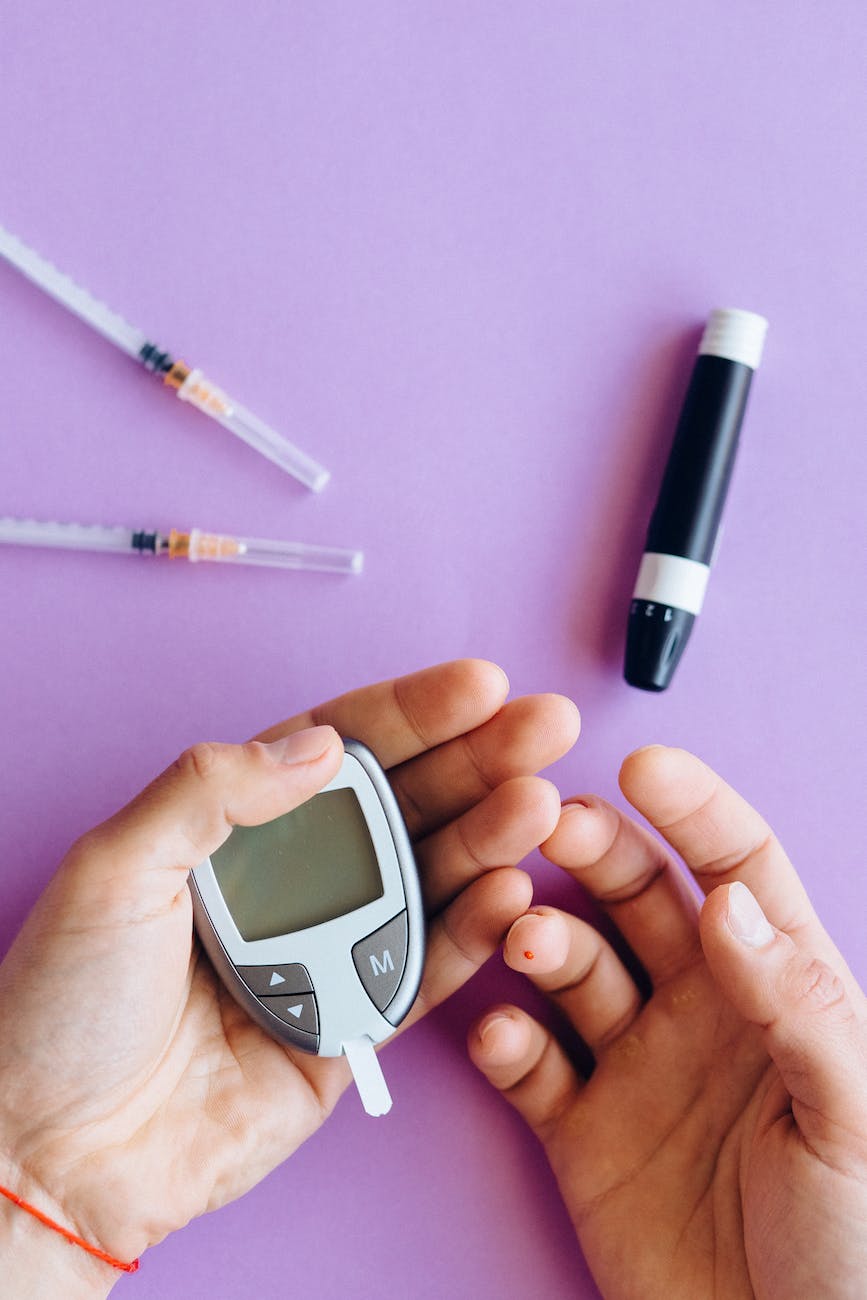
Type 2 diabetes is a common condition that requires careful management. This article provides an overview of type 2 diabetes treatment, covering lifestyle changes, medication options, and strategies to prevent complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is essential in developing an individualized treatment plan. Managing blood sugar levels, adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, and monitoring sugar levels are vital components. Stay informed about cardiovascular health, kidney health, neuropathy, eye health, and foot care. Access additional resources and support from reputable institutions and healthcare providers.
- Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes and treatment
- Treatment and management of type 2 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes treatment and prevention
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes treatment
- Type 2 diabetes and treatment
- Treatment and management of type 2 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes treatment and prevention
- Additional Resources and Support
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body metabolizes glucose. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type, characterized by the body's inability to properly use insulin or produce enough of it. Understanding the key aspects of type 2 diabetes can help individuals manage their condition effectively.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, allowing cells to absorb glucose for energy. Without sufficient insulin, blood sugar levels can rise and cause various health issues over time.
Causes and Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Multiple factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. These include genetics, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions. Modifiable risk factors such as sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy eating habits, and obesity significantly increase the chances of developing type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes often develops slowly, and its symptoms can be subtle or go unnoticed. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow wound healing. Diagnosis involves blood tests, including the A1C test, random blood sugar test, and oral glucose tolerance test.
Complications of Untreated Type 2 Diabetes
If left untreated or poorly managed, type 2 diabetes can lead to various complications. These complications can affect multiple organs and systems in the body, including the heart, kidneys, nerves, eyes, and feet. They may include heart disease, kidney disease, neuropathy, diabetic retinopathy, and foot problems.
- Cardiovascular Health and Blood Pressure Control:
- Kidney Health and Diabetic Nephropathy:
- Diabetic Neuropathy and Nerve Damage:
- Eye Health and Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Foot Care and Diabetic Foot Problems:
Proper management of type 2 diabetes, including lifestyle changes, regular medical check-ups, and adherence to treatment plans, can help prevent or minimize the risk of complications.
Type 2 diabetes and treatment
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). With type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn't produce enough insulin, or it resists insulin. Treatment for this condition involves a combination of lifestyle changes, monitoring blood sugar levels, and potentially medication or insulin therapy. The management of type 2 diabetes is crucial, as it can help prevent or delay complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and nerve damage. An effective treatment plan is personalized, taking into account the individual's health status, lifestyle, and preferences. By understanding the various options and working closely with healthcare providers, those with type 2 diabetes can lead full and active lives.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Fundamental changes such as adopting a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are pivotal in managing type 2 diabetes.
Blood Sugar Monitoring:
Regularly checking glucose levels helps to manage diabetes effectively and make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
Oral Medications:
There are different types of oral drugs that can help manage blood sugar levels, each working in unique ways to reduce glucose in the bloodstream.
Insulin Therapy:
Some people with type 2 diabetes may require insulin injections to help their bodies use glucose for energy.
Education and Support:
Being informed about the condition and having access to support can improve self-management and quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Regular Healthcare Consultations:
Ongoing medical care including routine check-ups, eye exams, and foot care, are essential for monitoring and preventing complications.
Cardiovascular Health:
Since diabetes increases the risk of heart problems, managing blood pressure and cholesterol is also a critical part of treatment.
Weight Management Programs:
These programs can assist in achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, a significant factor in controlling type 2 diabetes.
Medication Adherence:
Consistently taking prescribed medications according to the healthcare provider's instructions is key to managing the disease.
Advanced Treatment Options:
In some cases, bariatric surgery or advanced drug therapies may be considered for more effective diabetes management.
Treatment and management of type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes management
The cornerstone of type 2 diabetes management is often lifestyle modification, which includes a combination of diet, exercise, and weight control. Dietary changes focus on reducing the intake of sugars and refined carbohydrates, while increasing dietary fiber and whole grains. Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels. Moreover, weight loss for those who are overweight can have a profound effect on improving glycemic control and reducing the need for medication.
Individualized based on a patient's specific health profile
Medication management is another critical aspect of treating type 2 diabetes. Metformin is usually the first-line medication prescribed, as it helps to reduce glucose production in the liver and improve insulin sensitivity. If metformin alone is insufficient, other medications, including sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors may be added. The choice of medication is individualized based on a patient's specific health profile and needs.
Keeping blood glucose levels within target ranges
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) allows patients to adjust their diet, exercise, and medications based on readings. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems provide a more comprehensive picture of glucose trends throughout the day and night. Keeping blood glucose levels within target ranges can help prevent the long-term complications of diabetes, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
Telemedicine
Advancements in technology have also played a significant role in the management of type 2 diabetes. The use of digital health tools, such as smartphone apps and online platforms, can assist patients in tracking their food intake, physical activity, and medication schedules. Telemedicine has become increasingly valuable, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing for remote consultations and ongoing support from healthcare providers, which is particularly beneficial for managing a chronic condition like diabetes.
Finally, education and support are indispensable elements of effective diabetes management. Patients who understand the nature of their condition, the impact of lifestyle choices on their health, and the importance of adherence to their treatment plan are more likely to achieve successful long-term outcomes. Support from healthcare professionals, diabetes educators, and peer groups can motivate patients to maintain the daily commitments necessary for managing type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes treatment and prevention
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). With the number of individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes on the rise globally, it is crucial to understand the treatments and prevention strategies that can manage or even mitigate the condition. Effective management of type 2 diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Prevention, on the other hand, focuses on addressing the risk factors before the disease develops. In this article, we delve into the various options available to those living with type 2 diabetes and discuss strategies to prevent its onset, ensuring that patients can lead healthy, fulfilling lives despite the diagnosis.
Lifestyle Changes:
Adopt a nutritious diet rich in whole foods and low in processed sugars and fats to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Regular Physical Activity:
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week to improve insulin sensitivity.
Weight Management:
Aim for a healthy body weight to reduce resistance to insulin and decrease the risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
Medications:
Utilize medications such as metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists as prescribed to help control blood glucose levels.
Monitoring:
Keep a close eye on blood glucose levels with regular testing to make informed decisions about diet, activity, and medication.
Educational Programs:
Participate in diabetes education and support programs to better understand and manage the disease.
Prevention Strategies:
For those at risk, focus on prediabetes interventions, including lifestyle changes and medications, to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Annual Check-Ups:
Regular health screenings can detect early signs of diabetes or its complications, allowing for prompt and effective intervention.
By incorporating these treatment and prevention strategies into daily life, individuals can gain control over type 2 diabetes and reduce the risk of serious health complications associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes involves a comprehensive approach that focuses on lifestyle changes, developing an individualized treatment plan, and preventing and managing potential complications. By implementing these strategies, individuals with type 2 diabetes can improve their overall well-being and effectively manage their condition.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Importance of a Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced and healthy diet is essential for managing type 2 diabetes. It is crucial to focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods and limiting the intake of processed and sugary foods. Following a diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and support overall health.
Regular Exercise and Weight Management
Engaging in regular physical activity is beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes. Choosing activities that increase heart rate, such as walking, swimming, cycling, or running, can help improve insulin sensitivity and effectively manage blood sugar levels. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through physical activity and proper nutrition can further enhance diabetes management.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Frequent monitoring of blood sugar levels using devices like glucose meters is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. It allows individuals to track and understand how various factors, such as diet, exercise, and medication, affect their blood sugar levels. Continuous glucose monitoring, which provides real-time glucose readings and transmits data to a mobile device, is another option for enhanced monitoring.
Medication and Insulin Therapy
In some cases, medication or insulin therapy may be necessary to manage type 2 diabetes effectively. Oral medications and injectables are available options that can help control blood sugar levels. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate medication regimen and ensure its proper use.
Developing an Individualized Treatment Plan
Developing an individualized treatment plan involves working closely with healthcare providers to create a comprehensive approach tailored to each person's unique needs and goals. This includes regular check-ups, blood tests, and adjusting treatment plans as necessary. Considerations such as overall health, medical history, lifestyle factors, and personal preferences play a significant role in developing an effective and personalized treatment strategy.
Preventing and Managing Complications
Cardiovascular Health and Blood Pressure Control
Maintaining cardiovascular health is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Implementing lifestyle habits such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and managing blood pressure levels can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and related complications.
Kidney Health and Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy, a kidney complication, is a concern for people with type 2 diabetes. Managing blood sugar levels, controlling blood pressure, and regular monitoring can help prevent or slow the progression of kidney disease. Close monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to ensure early detection and appropriate management.
Diabetic Neuropathy and Nerve Damage
Preventing and managing diabetic neuropathy involves maintaining stable blood sugar levels and managing associated risk factors. Regular foot care and seeking medical attention for any signs or symptoms of nerve damage are essential for preventing complications and promoting overall well-being.
Eye Health and Diabetic Retinopathy
Regular eye examinations and maintaining stable blood sugar levels are crucial for preventing and managing diabetic retinopathy. Working closely with eye care professionals can help individuals with type 2 diabetes detect and treat any eye-related complications early.
Foot Care and Diabetic Foot Problems
Proper foot care is essential for individuals with type 2 diabetes to prevent foot complications. This involves daily inspection, wearing comfortable and supportive footwear, and seeking prompt medical attention for any signs of infection or abnormalities.
By implementing lifestyle changes, developing an individualized treatment plan, and actively preventing and managing complications, individuals with type 2 diabetes can take control of their health and effectively manage their condition.
Type 2 diabetes treatment
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). With the number of individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes on the rise, effective management and treatment options are more critical than ever. Treatment for this condition involves a combination of lifestyle changes, monitoring blood glucose levels, and potentially, medication or insulin therapy. The goal is to maintain normal blood glucose levels and prevent or manage complications. Understanding the various treatment options available can empower individuals to take an active role in managing their condition and improving their quality of life. Below is a list of treatment elements for type 2 diabetes, highlighting the multi-faceted approach to managing this disease.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Fundamental changes such as adopting a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are pivotal in managing type 2 diabetes.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose levels helps to track the effectiveness of treatment and make necessary adjustments.
- Medications: Oral medications, like metformin, are often prescribed to help control blood glucose levels. Other drugs may target different aspects of diabetes management.
- Insulin Therapy: Some patients may require insulin injections to maintain optimal blood glucose control.
- Education and Support: Diabetes education programs and support groups can be invaluable in helping individuals understand and manage their condition.
- Regular Health Check-Ups: Routine visits to healthcare providers for comprehensive check-ups to monitor for diabetes-related complications.
- Advanced Treatment Options: These may include bariatric surgery for eligible individuals or the use of newer medications such as GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: For some, using CGM systems can provide detailed insights into glucose patterns and trends, aiding in tighter glucose management.
Type 2 diabetes and treatment
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). With type 2 diabetes, the body either resists the effects of insulin — a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into your cells — or doesn't produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Treatment for this condition is multifaceted, often requiring lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes even surgery to effectively manage and maintain blood sugar levels. An individualized approach is crucial, as each person's body responds differently to various treatments. Keeping type 2 diabetes under control is essential to prevent potential complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney damage. Below, we explore the various options available for managing and treating type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Incorporating a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and weight management are foundational steps in treating type 2 diabetes.
- Medication: Metformin is often the first medication prescribed for type 2 diabetes, with other drugs added if needed to achieve blood sugar control.
- Insulin Therapy: Some individuals may require insulin injections when oral medications are not sufficient.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar: Regularly checking blood glucose levels allows for timely adjustments in treatment.
- Bariatric Surgery: In selected cases, particularly for those with obesity and difficulty managing diabetes, bariatric surgery may be an option.
- Educational and Support Programs: Education about diabetes and ongoing support can improve management and outcomes.
- Novel Therapeutics: Research continues to bring new treatment options, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine medical appointments are important for monitoring overall health and managing diabetes-related complications.
Remember, effective management of type 2 diabetes requires a collaborative effort between healthcare providers and the patient. It's about finding the right balance of treatments to maintain blood sugar levels and prevent complications while also accommodating the patient's lifestyle and preferences.
Treatment and management of type 2 diabetes
The treatment and management of type 2 diabetes are multifaceted and tailored to individual needs. Effective management often requires a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication. Lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating, regular physical activity, and weight management, are foundational to controlling blood sugar levels. For many, these changes may be supplemented with oral medications or insulin therapy to achieve optimal glucose control. Furthermore, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and ongoing consultations with healthcare professionals can help patients maintain their health and prevent complications associated with this chronic condition. It's essential for patients to understand that managing type 2 diabetes is a continuous process that might require adjustments over time as their condition changes.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Includes diet changes, increased physical activity, and weight loss strategies.
- Medications: Oral drugs (like metformin), insulin injections, and newer classes of medications that affect insulin sensitivity or urinary glucose excretion.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regular self-testing to track blood sugar levels and adjust treatment accordingly.
- Education and Support: Patient education on self-management practices and access to support groups or counseling.
- Regular Check-Ups: Ongoing assessments with healthcare providers to monitor HbA1c levels and other health indicators.
- Cardiovascular Health Management: Control of blood pressure and cholesterol levels to reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Prevention of Complications: Regular screening for complications such as neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Adjustments in therapy based on individual patient response and changes in their condition.
- Technology Integration: Use of apps and devices for tracking health data and medication reminders.
Type 2 diabetes treatment and prevention
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). With the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes worldwide, effective management and prevention strategies are more critical than ever. Treatment often requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring to prevent complications. Prevention focuses on addressing the risk factors that can lead to diabetes, such as obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. Through a combination of proactive measures and medical interventions, individuals with type 2 diabetes can lead a healthy life and minimize the risk of associated health issues.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular physical activity and a healthy diet are the cornerstones of both diabetes management and prevention.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and help manage the condition effectively.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly checking blood glucose levels helps to keep track of diabetes control and prevent long-term complications.
- Medications: Various medications, including metformin and insulin, may be prescribed to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Educational Resources: Access to diabetes education can empower individuals to make informed choices about their health and treatments.
- Regular Healthcare Visits: Routine check-ups with healthcare professionals are vital for monitoring the condition and adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
- Prevention Programs: Participating in structured programs can support individuals at risk for diabetes to make lasting lifestyle changes.
Additional Resources and Support
For individuals seeking comprehensive diabetes treatment and support, Mayo Clinic offers a range of additional resources and services to assist patients in managing their Type 2 diabetes effectively.
Mayo Clinic's Approach to Diabetes Treatment
At Mayo Clinic, our multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals is dedicated to providing personalized and evidence-based diabetes care. Our approach focuses on education, self-management, and collaborative decision-making between patients and their healthcare providers. We prioritize individualized treatment plans that address the unique needs and goals of each patient.
Educational Opportunities and Resources for Patients
Mayo Clinic offers a variety of educational programs and resources designed to empower patients with the knowledge and skills necessary to successfully manage their Type 2 diabetes. From structured diabetes education classes to interactive online resources, we provide access to the latest information and tools to support self-care and improve health outcomes.
Mayo Clinic's Research and Clinical Trials
As a leading medical institution, Mayo Clinic is actively involved in conducting research and clinical trials to advance the understanding of Type 2 diabetes and develop innovative treatment approaches. Patients have the opportunity to participate in cutting-edge research studies and clinical trials, contributing to the development of new therapies and interventions.
International Patient Services and Support
Mayo Clinic extends its expertise and support to international patients seeking diabetes treatment. Our dedicated International Patient Services team assists with travel arrangements, medical appointments, language interpretation, and other logistical needs. We strive to provide a seamless experience and ensure that international patients receive the highest quality of care.
Financial Assistance and Charitable Care Options
Mayo Clinic is committed to providing accessible and affordable diabetes treatment to all individuals, regardless of their financial circumstances. We offer various financial assistance programs and charitable care options to help alleviate the financial burden associated with healthcare expenses. Our financial counselors work closely with patients to explore available resources and find suitable solutions.
Staying Connected with Mayo Clinic
Stay connected with Mayo Clinic for the latest updates and valuable resources related to Type 2 diabetes treatment. Download our user-friendly mobile app to access personalized health information, appointment reminders, and educational materials. Connect with us through various social media channels to join a community of individuals dedicated to managing their diabetes and achieving optimal health.
Our top advice is to consult professionals for revolutionary diabetes guidance to drastically improve your health.
Visit at this time the link that keeps clicking on it