Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment - Empowering Individuals to Live Healthy Lives

Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment - Empowering Individuals to Live Healthy Lives
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on diabetes, its diagnosis, and treatment options. At https://diabetescure4u.com/, we believe in empowering individuals to lead healthy lives, and this article aims to provide you with valuable insights into managing diabetes effectively. With a wealth of information at your fingertips, we are confident that this article, Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment - Empowering Individuals to Live Healthy Lives, will help you gain a better understanding of this condition and support you in making informed decisions about your health.
Understanding Diabetes
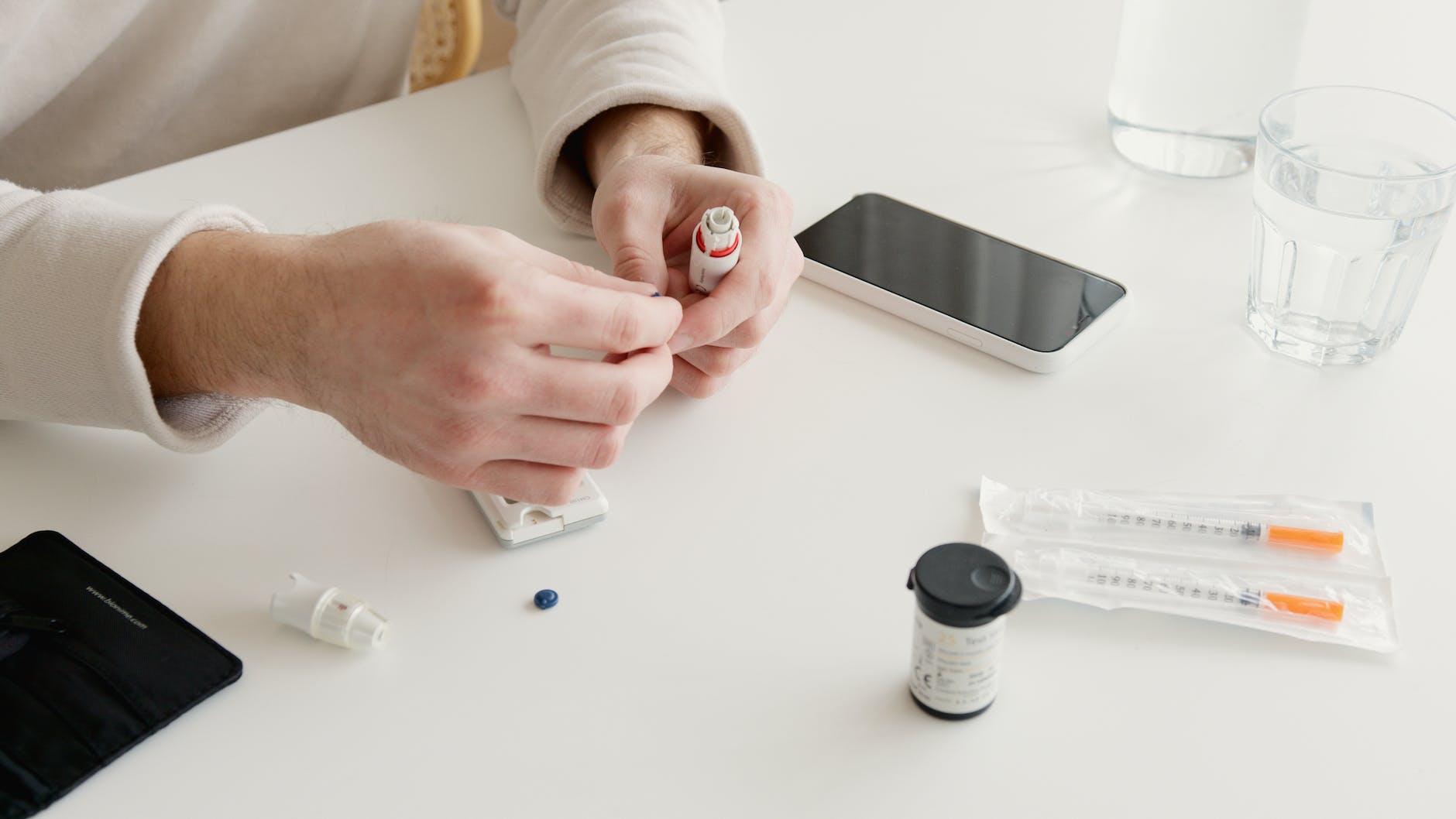
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood glucose levels. It occurs when the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, allowing glucose to enter cells and provide energy. Without proper management, diabetes can lead to various health complications.
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: This type of diabetes typically develops in childhood or early adulthood and is caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking and destroying the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections for survival.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is more common and often occurs later in life. It is primarily linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and excess weight. In this condition, the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas may not produce enough insulin to compensate.
- Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes affects pregnant women who have high blood glucose levels. Although it usually resolves after childbirth, it increases the risk of type 2 diabetes later in life for both the mother and child.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for effective management. Some common symptoms to watch out for include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. The diagnosis involves various tests, including blood sugar level measurements, oral glucose tolerance tests, and glycated hemoglobin (A1C) tests.
Treatment and Management
Lifestyle Changes
Diet: A healthy diet plays a key role in managing diabetes. Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of sugary drinks, processed foods, and saturated fats. Consider working with a registered dietitian who specializes in diabetes management to develop a personalized meal plan.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and promotes overall health. Engage in aerobic activities like walking, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week. Additionally, strength training exercises can help build muscle and enhance glucose control.
Weight Management: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can significantly improve diabetes management. Even modest weight loss can have a positive impact on blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
Medications
Depending on the type and severity of diabetes, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to help manage your condition. These may include:
- Insulin: People with type 1 diabetes and some individuals with type 2 diabetes may require insulin therapy. It can be administered through injections or an insulin pump.
- Oral Medications: Various oral medications are available to lower blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes. These medications work in different ways, such as increasing insulin production, reducing glucose production, or improving insulin utilization.
Monitoring and Support
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial for diabetes management. Your healthcare provider will guide you on how frequently to test your blood sugar and what target levels to aim for. Additionally, they may recommend periodic tests to assess your overall health, such as cholesterol and kidney function tests.
It is also beneficial to seek support from healthcare professionals, diabetes educators, and support groups. They can provide valuable guidance, education, and emotional support throughout your journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes is a complex condition that requires careful management. By understanding the different types of diabetes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can take control of their health and minimize the risk of complications. With the guidance of healthcare professionals, appropriate medication, and regular monitoring, it is possible to live a fulfilling life while effectively managing diabetes.
Remember, knowledge is power, and the more you educate yourself about diabetes, the better equipped you are to make informed decisions about your health. At [Your Company Name], we are committed to supporting you on this journey and providing you with the resources you need to live a healthy and fulfilling life. https://diabetescure4u.com/
- Understanding the Relationship Between A1C Levels and Blood Sugar Control
- Causes of Type 1 Diabetes: Understanding the Underlying Factors
- The Different Types of Blood Sugar Tests and How They Are Performed
- Oral Medications for Diabetes: Metformin, Sulfonylureas, and More
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: A Comprehensive Guide


