A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes: New Breakthroughs & Hope for US



- A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes: New Breakthroughs & Hope for US
- Is There A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes?
- Overview of A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes
- Understanding the Need for A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes
- Latest News on Type 1 Diabetes Research
- Treatment Options and Management of Type 1 Diabetes
- Promising New Developments in Type 1 Diabetes Research
- Living with Type 1 Diabetes: Strategies and Support
- Future Outlook and Potential for a Cure
A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes: New Breakthroughs & Hope for US
A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes is something that many have been seeking for years. Type 1 diabetes affects millions in the US, necessitating the search for a cure. Understanding this chronic autoimmune disease is crucial, as the pancreas produces insufficient insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Various ongoing research efforts offer hope for A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes, such as stem cell therapy advancements, clinical trials, and islet transplantation.
Treatment options, like insulin therapy and artificial pancreas systems, help manage the condition. Exciting developments are emerging, like immune system modulation breakthroughs and beta cell regeneration. Strategies for coping with daily challenges and emotional support for patients are also discussed. The future outlook holds promise for A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes, emphasizing the need for funding and collaboration within the US community.
Is There A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes?
When it comes to type 1 diabetes, finding A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes is a paramount objective. This chronic autoimmune disease, characterized by insufficient insulin production in the pancreas, leads to high blood sugar levels. While managing the condition with insulin therapy and other treatments is possible, the ultimate goal is to discover A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes that eliminates the dependence on external insulin.
Overview of A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition that typically develops in childhood or adolescence. Unlike type 2 diabetes, it is not linked to lifestyle factors or obesity. In type 1 diabetes, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, resulting in low or no insulin production. This deficiency of insulin leads to an accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream, causing high blood sugar levels.
Understanding the Need for A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes
The search for A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes is driven by the desire to eradicate the limitations and complications associated with the disease. While current treatment options can help manage blood sugar levels, they do not address the underlying cause of the condition or provide a permanent solution. A Cure for Type 1 Diabetes would allow individuals with type 1 diabetes to lead healthier, more unrestricted lives, free from the constant monitoring and administration of insulin.
The efforts to discover a cure involve extensive research and advancements in various fields, including stem cell therapy, clinical trials, and islet transplantation. These promising avenues of investigation continue to fuel optimism within the scientific community and offer potential pathways towards a cure for type 1 diabetes.
In the following sections, we will explore the latest news and advancements on type 1 diabetes research, treatment options available, and the promising new developments that hold hope for those seeking a long-term cure.
Latest News on Type 1 Diabetes Research
Keeping up with the latest advancements in type 1 diabetes research is crucial to understand the potential for a cure. Scientists and medical professionals are working tirelessly to explore various avenues and make significant progress in this field.
Advances in Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy holds great promise in the quest for a cure for type 1 diabetes. Researchers are investigating the ability of stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Exciting breakthroughs have been made in using embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells for this purpose. While challenges remain, early results from preclinical and clinical studies offer hope for a future cure.
Clinical Trials for Potential Cure
Clinical trials play a crucial role in evaluating new treatment approaches and potential cures for type 1 diabetes. These trials involve rigorous testing of innovative therapies and interventions in humans. Researchers are conducting trials to assess the safety and effectiveness of various methodologies, such as immunotherapy, gene therapy, and novel drug compounds. Participating in clinical trials not only provides patients with access to cutting-edge treatments but also contributes to advancing medical knowledge in the pursuit of a cure.
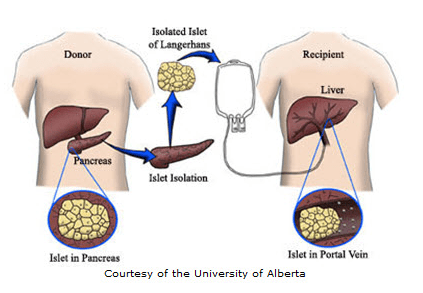
Islet Transplantation and Beta Cell Replacement
To overcome the shortage of insulin-producing beta cells, researchers are investigating islet transplantation and beta cell replacement therapies. Islet transplantation involves transferring healthy islet cells from donors into individuals with type 1 diabetes, aiming to restore insulin production. Advances in islet isolation techniques and immune-suppression strategies have improved the success rate of such procedures. Additionally, efforts are underway to create artificial beta cells, including encapsulation techniques and the use of cell-reprogramming approaches. These innovative approaches hold promise for long-term sustainable solutions in curing type 1 diabetes.
Continuing research and advancements in stem cell therapy, clinical trials, islet transplantation, and beta cell replacement provide hope for individuals with type 1 diabetes in the United States. Collaboration between researchers, healthcare professionals, and organizations, along with adequate funding and advocacy, is crucial to accelerate progress and ultimately find a cure for this chronic disease.
Treatment Options and Management of Type 1 Diabetes


Type 1 diabetes requires diligent management and a multifaceted approach to maintain blood sugar control. Several treatment options are available to individuals living with this condition, aiming to mimic the functioning of a healthy pancreas and regulate blood glucose levels effectively. The following subsections provide an overview of key treatment strategies:
Insulin Therapy and Blood Sugar Control
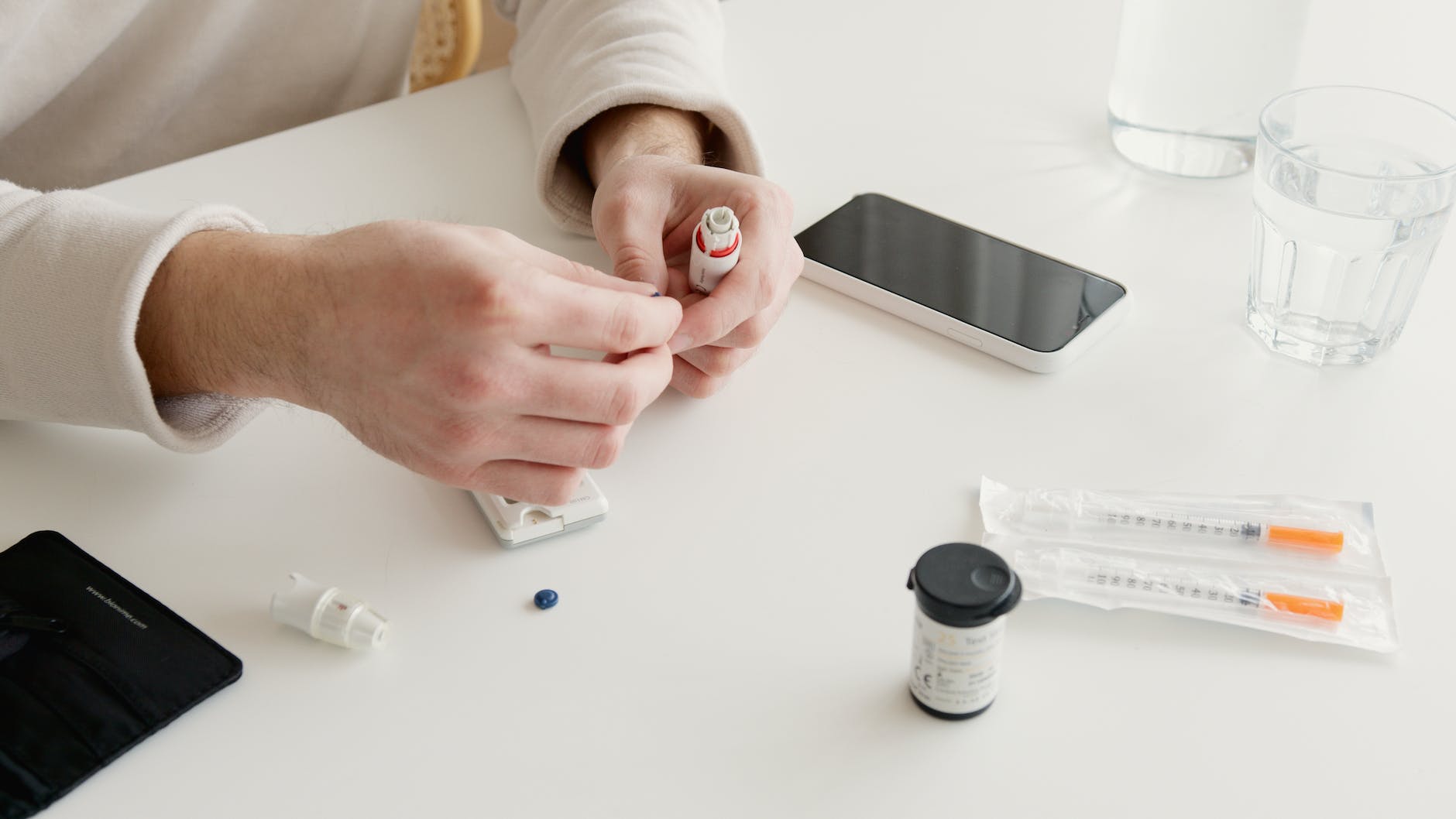

Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of managing type 1 diabetes. Daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump helps to regulate blood sugar levels and maintain optimal glycemic control. Multiple types of insulin are available, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin. The type and dosage of insulin required may vary based on an individual's needs and daily blood sugar monitoring.
- Insulin injections or pump therapy aims to provide basal (background) insulin and mealtime bolus insulin to mimic the natural insulin production of a healthy pancreas.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices can be used to track blood sugar levels in real-time, providing valuable insights for adjusting insulin doses and managing glucose fluctuations.
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels through fingerstick testing is crucial for making informed insulin dosing decisions and maintaining stable glycemic control.
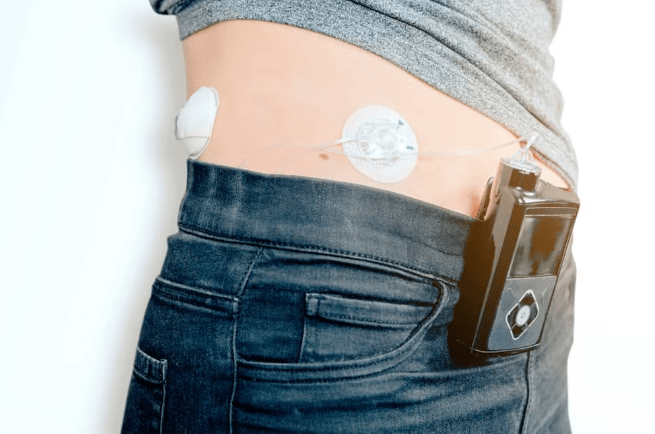
Artificial Pancreas Systems
Artificial pancreas systems, also known as closed-loop systems, have emerged as an innovative approach to automate insulin delivery in people with type 1 diabetes. These systems combine continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology with an insulin pump, controlling insulin delivery based on real-time blood sugar levels. This closed-loop system offers a more precise and automated way to regulate blood sugar, reducing the burden of constant monitoring and manual insulin adjustments.
- The artificial pancreas uses algorithms to calculate the appropriate insulin dose and adjust it automatically based on CGM data.
- Continuous monitoring of blood sugar levels allows for the timely detection and prevention of both hypo- and hyperglycemia.
- Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to refine these systems, improving accuracy and optimizing user experience.
Innovative Approaches to Insulin Delivery
Researchers are exploring alternative methods of insulin delivery to enhance convenience and improve glycemic control in type 1 diabetes.
- Insulin patches, inhalers, or oral formulations are being investigated as non-injectable alternatives, potentially offering new options for insulin administration.
- Smart insulin pens and connected insulin delivery devices allow for customized dosing, dose tracking, and data integration to facilitate diabetes management.
- Advancements in insulin pump technology, such as smaller and more discreet pumps with advanced features, are making insulin therapy more convenient and user-friendly.
Effective treatment options that address the specific needs of individuals with type 1 diabetes play a crucial role in achieving optimal glycemic control and improving quality of life. Continued research and technological innovations aim to further refine treatment methods and ultimately contribute to the advancement of a cure for type 1 diabetes.
Promising New Developments in Type 1 Diabetes Research
Advancements in type 1 diabetes research offer hope for finding a potential cure. Scientists and medical professionals are exploring various approaches to improve the lives of individuals affected by this condition.
Breakthroughs in Immune System Modulation
Researchers are making significant progress in understanding how the immune system plays a role in type 1 diabetes. Exciting breakthroughs include the identification of new immune-modulating therapies that aim to stop or prevent the autoimmune response attacking the pancreatic cells responsible for insulin production.
These innovative treatments involve balancing the immune system's response, reducing inflammation, and preserving beta cell function. By modulating the immune system, these therapies hold promise in slowing down or halting the progression of the disease.
Regeneration of Beta Cells
Regenerating beta cells, which are crucial for insulin production, is an area of intense research focus. Scientists are exploring different strategies to stimulate the regeneration of these cells, potentially leading to restored insulin production in individuals with type 1 diabetes.
Several approaches, such as stem cell therapy, gene editing, and beta cell replication, show promise in restoring beta cell function. These regenerative therapies aim to provide a long-term solution for managing type 1 diabetes naturally by replenishing the insulin-producing cells within the pancreas.
Alternative Therapies for Long-Term Cure
In addition to immune system modulation and beta cell regeneration, researchers are exploring alternative therapies that could potentially offer a long-term cure for type 1 diabetes. These therapies involve innovative techniques such as tissue engineering, nanotechnology, and precision medicine.
Experimental treatments like islet encapsulation and artificial pancreas devices continue to evolve, aiming to provide individuals with more effective ways to manage their blood sugar levels and lead a healthier life. These alternative therapies offer potential solutions beyond traditional insulin therapy, providing hope for a future where individuals with type 1 diabetes can live free from the burden of daily management.
As research progresses, these promising developments in type 1 diabetes research bring us closer to finding a cure and improving the lives of millions of Americans affected by this chronic condition.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes: Strategies and Support
Living with type 1 diabetes requires effective strategies and a strong support system. Coping with the challenges of daily management, understanding the role of diet and exercise in glycemic control, and seeking emotional and psychological support are essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Coping with the Challenges of Daily Management
Managing type 1 diabetes on a daily basis can be overwhelming, but there are strategies that can help. Some key approaches include:
- Developing a consistent routine for monitoring blood sugar levels and administering insulin.
- Learning how to calculate carbohydrates and adjust insulin doses accordingly.
- Keeping a record of blood sugar levels, insulin doses, and meals to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments.
- Being prepared for unexpected situations, such as carrying snacks or glucose tablets in case of low blood sugar episodes.
- Regularly visiting healthcare professionals to track progress and receive guidance.
The Role of Diet and Exercise in Glycemic Control
A healthy diet and regular exercise play a vital role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels for individuals with type 1 diabetes. Here are some important considerations:
- Working with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan that focuses on nutrient-rich foods and portion control.
- Monitoring carbohydrate intake and spreading it evenly throughout the day to minimize blood sugar fluctuations.
- Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines, with guidance from healthcare professionals. Exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and overall well-being.
- Being aware of how different foods and physical activities affect blood sugar levels and adjusting insulin doses accordingly.
- Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to ensure safety and optimal glycemic control.
Emotional and Psychological Support for Patients
Maintaining emotional well-being is crucial for individuals living with type 1 diabetes. People with diabetes may experience stress, anxiety, and other emotional challenges. Here are some strategies for seeking support:
- Connecting with support groups or online communities of individuals with type 1 diabetes. Sharing experiences, concerns, and solutions can provide reassurance and practical advice.
- Seeking professional counseling or therapy to address emotional challenges associated with diabetes management.
- Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or hobbies that bring joy and relaxation.
- Communicating openly with family, friends, and healthcare providers about diabetes-related concerns and seeking their understanding and support.
- Staying informed about the latest research and advancements in type 1 diabetes care, which can offer hope and inspiration.
Overall, living with type 1 diabetes requires a holistic approach that encompasses effective daily management strategies, proper nutrition, regular exercise, and emotional well-being. By integrating these strategies into daily life, individuals with type 1 diabetes can lead fulfilling lives while managing their condition.
Future Outlook and Potential for a Cure
Looking ahead, there is great promise in finding a cure for type 1 diabetes. Ongoing research efforts are exploring several exciting directions that offer hope for individuals living with this condition.
Promising Directions in Research
In recent years, scientific advancements have paved the way for innovative approaches in tackling type 1 diabetes. One area of focus is the development of novel immunotherapies that aim to modulate the immune system's response, preventing it from attacking the pancreatic cells responsible for insulin production. Additionally, regenerative medicine holds potential, with researchers exploring ways to regenerate beta cells, which would restore the body's ability to produce insulin naturally.
Importance of Funding and Advocacy
To turn these promising avenues into reality, adequate funding and advocacy are crucial. Government agencies, private organizations, and philanthropic efforts need to prioritize and invest in type 1 diabetes research. Raising awareness and advocating for increased funding can pave the way for breakthroughs and accelerate the search for a cure.
Collaboration and Community Involvement
Achieving a cure for type 1 diabetes requires collaboration among researchers, healthcare providers, and the patient community. By fostering collaborative partnerships and sharing knowledge, the chances of developing effective treatments and ultimately finding a cure are significantly enhanced. Strong community involvement, including participation in clinical trials and support for research initiatives, plays a vital role in advancing the field.
As we move forward, it is essential to remain optimistic about the potential for a cure for type 1 diabetes. By prioritizing research, advocating for adequate funding, and fostering collaboration, we can continue making significant strides towards a future where individuals living with type 1 diabetes can lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.